Figure 7. Proposed activation mechanism for Olfr73 and Olfr74.
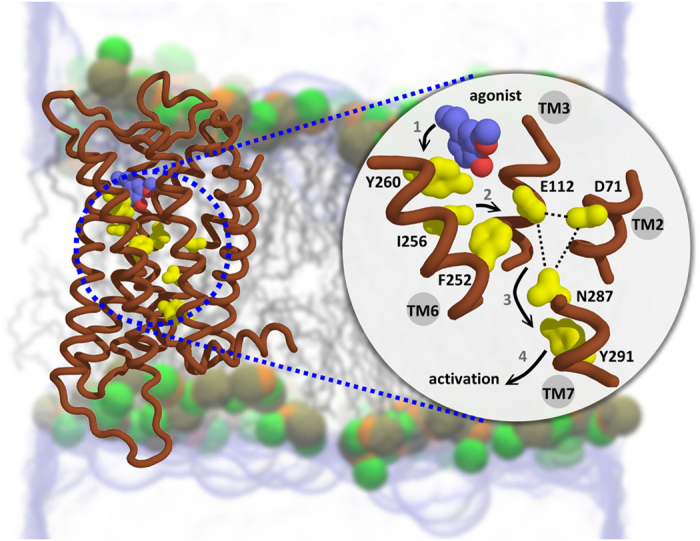
The binding of an agonist induces a molecular switch at position 260 (TM6) (step 1) which is further transferred to I256 and F252 along TM6 deeper into the receptor structure (step 2). Conformational fluctuations of F252 may have functional impact on the solvent mediated hydrogen bond network formed between E112 (TM3), D71 (TM2) (2.50) and N287 (TM7) (locates in NPxxY motif) (step 3). The interruption of this network can further lead to the breaking of hydrogen bonds between N287 (TM7) and Y291 (TM7). The switches of Y291 are coupled to the movement of TM7 to induce the dissociation of the G-protein, bound to Y291 (step 4).
