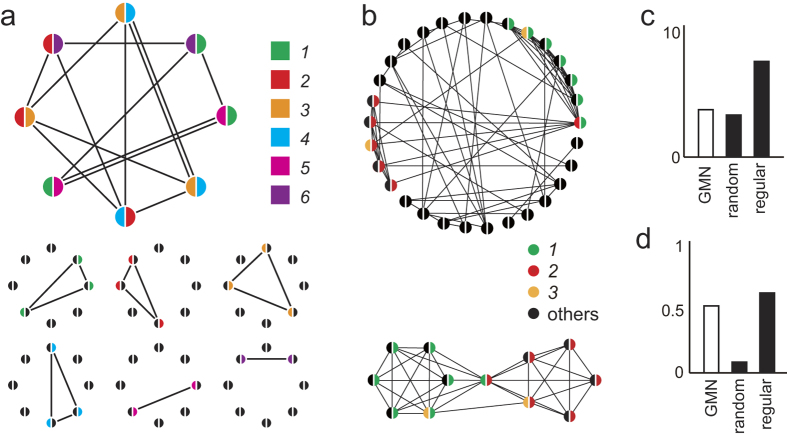
Figure 1. Characteristics of the circular GMN.
(a) A GMN with eight neurons, each of which expressed two genes from a repertoire of six genes (colors). Neurons expressing common gene(s) were connected. Subnetworks connected by a single gene are shown below. A subnetwork connected by a single gene expressed in three neurons formed a triangle or cluster (genes 1–4). (b) A GMN with 30 neurons, each of which randomly expressed 2 genes from a repertoire of 30 genes. Neurons expressing gene 1 (green) and gene 2 (red) were re-aligned and extracted from the GMN (below). Shortcuts made by neurons expressing both gene 1 and 2 or neurons expressing gene 3 (yellow) are shown. (c,d) The average shortest path length (c) and clustering coefficients (d) of a circular GMN with 100 neurons (GR = 50, GE = 5, open bars), a random network, and a regular network (lattice as in Watts and Strogatz, 1998). In the GMN used for c and d, one connection was defined even when a pair of neurons shared multiple common genes.