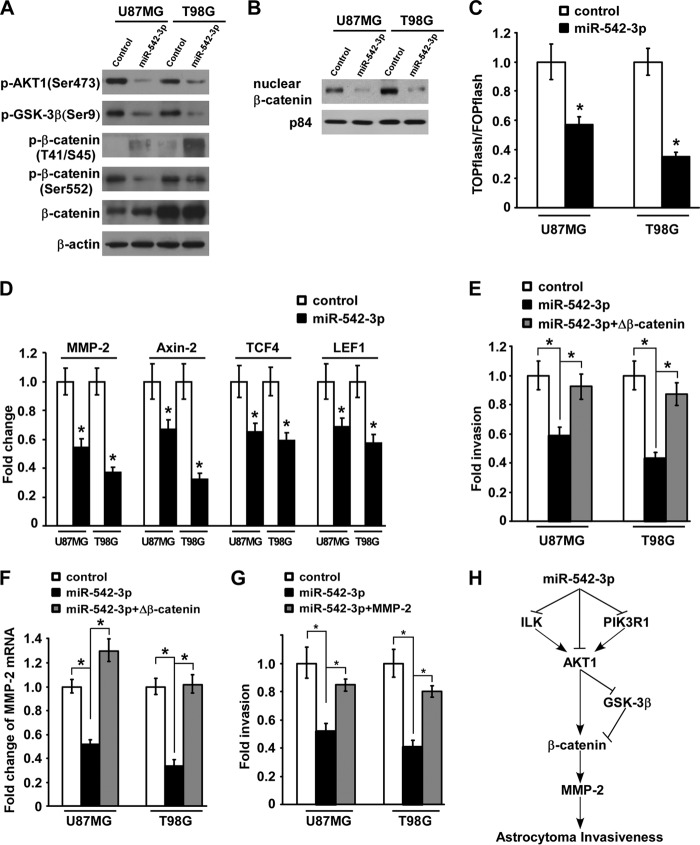
FIGURE 5.
Up-regulated miR-542-3p inhibits AKT1/β-catenin signaling pathway in glioblastoma cells to exert anti-invasive effect. A, Western blotting analysis of expression of phospho-AKT1 (p-AKT1) (Ser-473), phospho-GSK-3β (p-GSK-3β) (Ser-9), phospho-β-catenin (Thr-41/Ser-45), and phospho-β-catenin (Ser-552) in the indicated miR-542-3p-overexpressing cells and control cells. B, subcellular fractionation assay of nuclear β-catenin distribution in the indicated cells. p84 was used as loading control for extracted nuclear proteins. C, luciferase activity assays of TOPflash and FOPflash reporters in the indicated miR-542-3p-overexpressing cells and control cells. D, real time PCR quantification of several downstream genes of β-catenin signaling, including MMP-2, Axin2, TCF4, and LEF1, in the indicated miR-542-3p-overexpressing cells and control cells. E, the anti-invasive effect of ectopic miR-542-3p could be mostly reversed by overexpression of the constitutively active form of β-catenin (Δβ-catenin). F, real time PCR quantification of MMP-2 expression in the indicated miR-542-3p-overexpressing cells and control cells. G, MMP-2 re-expression by transfecting MMP-2-expressing plasmid in miR-542-3p-overexpressing glioblastoma cells markedly revived their invasive abilities. H, schematic model for miR-542-3p-mediated down-regulation of its target genes, namely ILK, PIK3R1, and AKT1; aberrant inhibition of the AKT/β-catenin/MMP-2 signaling cascade; and resultant suppression of astrocytoma invasiveness. Error bars represent mean ± S.D. derived from three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05.