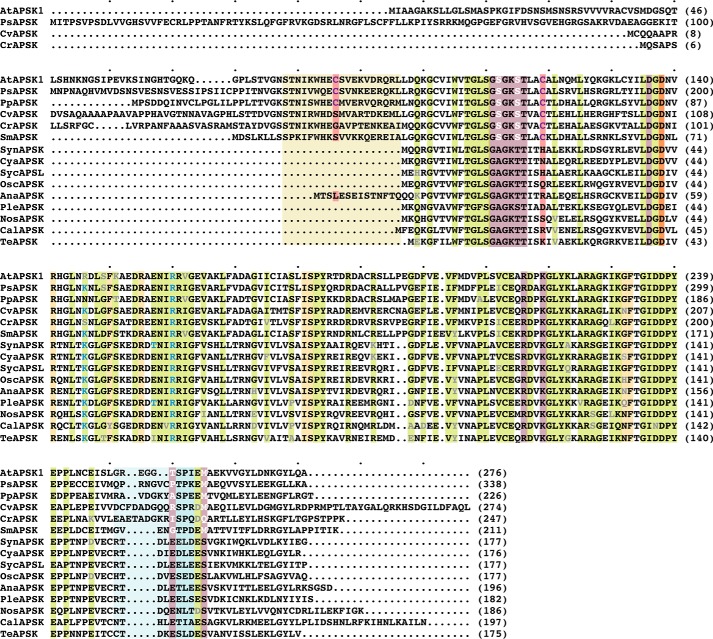
FIGURE 2.
Multiple sequence alignment of APSK from cyanobacteria, algae, mosses, and plants. Protein abbreviations are the same as given for Fig. 1C. Conserved residues are highlighted in green with variations indicated by gray text. Residues in the APS binding site and ATP binding site are highlighted in gold and rose, respectively. The invariant catalytic aspartate is highlighted in orange. Amino acid positions corresponding to residues in the disulfide linkage are highlighted in red. The tan box delineates residues corresponding to the NTD of AtAPSK. The light blue box indicates residues in the β1e-α7 loop. Residues corresponding to the sulfate binding site at the dimer interface of SynAPSK are indicated by light blue text. The multiple sequence alignment was generated with MultAlin.