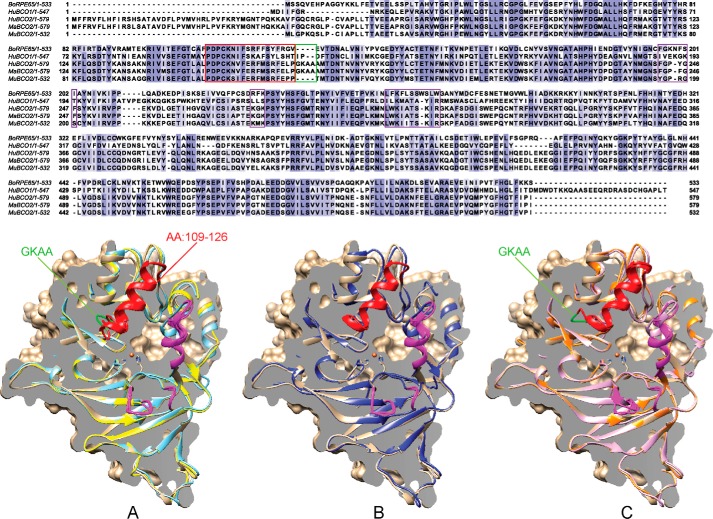
FIGURE 1.
Sequence and structure homology of CCOs. Top, alignment of bovine RPE65, human BCO1, human BCO2, macaque BCO2, and murine BCO2 is shown. The GKAA primate insertion is boxed in green, membrane binding domains are in magenta, and the previously unresolved amino acid (AA) 109–121 region is boxed in red. All structures are modeled using bovine RPE65 (tan) as template and are aligned facing into the active site with the Fe2+ iron cofactor denoted as an orange sphere. A comparison of three-dimensional structures of human BCO2 (light blue) and murine BCO2 (yellow) (A), chimeric human BCO2 (blue) (B), and wild-type (light purple) and chimeric (orange) macaque BCO2s (C) is shown. The four-amino acid insertion (GKAA) in primate BCO2s is colored green. The previously unresolved amino acid 109–126 region is colored red, and the presumed plasma membrane binding sites are highlighted in magenta.