FIGURE 1.
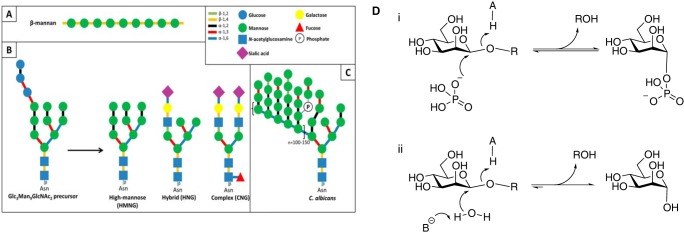
Schematic representation of the mannosides present in the human gut and reaction mechanisms of inverting glycoside phosphorylases and hydrolases. A, plant β-mannan, a hemicellulosic component of plant cell walls. B, human N-glycans, showing the different types of structures found on mature glycoproteins formed from a common Glc3Man9GlcNAc2 precursor. C, yeast mannan. The structure depicted here is that of C. albicans, containing β-1,2-linked mannosyl units that cap the side chains of the α-1,6-mannose backbone. D, general reaction mechanisms for inverting mannoside phosphorylases (panel i) and hydrolases (panel ii).
