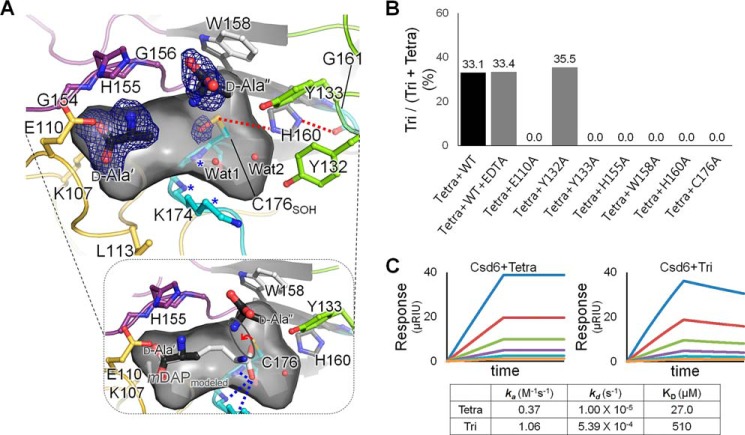
FIGURE 5.
d-Ala-complexed Csd6 and key residues for the l,d-CPase activity. A, ribbon diagram and the accessible inner surface of the active site in the Csd4-Ala structure. The bound d-Ala molecules (d-Ala′ and d-Ala″) (upper panel) and the mDAP (bottom panel) modeled on the basis of d-Ala′ and Wat1 are shown in stick models. The omit mFo − DFc maps for d-Ala′ and d-Ala″ (contoured at 2.0σ) and the side chain oxygen atom of Cys-176 oxidized as the sulfenic acid (contoured at 2.5σ) are colored in blue. The oxyanion hole is asterisked and also shown as blue dotted lines in the bottom panel. Red dotted lines indicate the interactions among residues of the catalytic triad. B, l,d-carboxypeptidation activities of the wild-type Csd6 (with the treatment of EDTA or not) and the mutants (E110A, Y132A, Y133A, H155A, W158A, H160A, and C176A) with the muramyl tetrapeptide. C, SPR experiments with immobilized Csd6 and the muramyl tetrapeptide (or muramyl tripeptide) as an analyte at different concentrations (15.6, 31.3, 62.5, 125, 250, and 500 μm) are shown in traces colored as orange, light blue, purple, green, red, and blue, respectively.