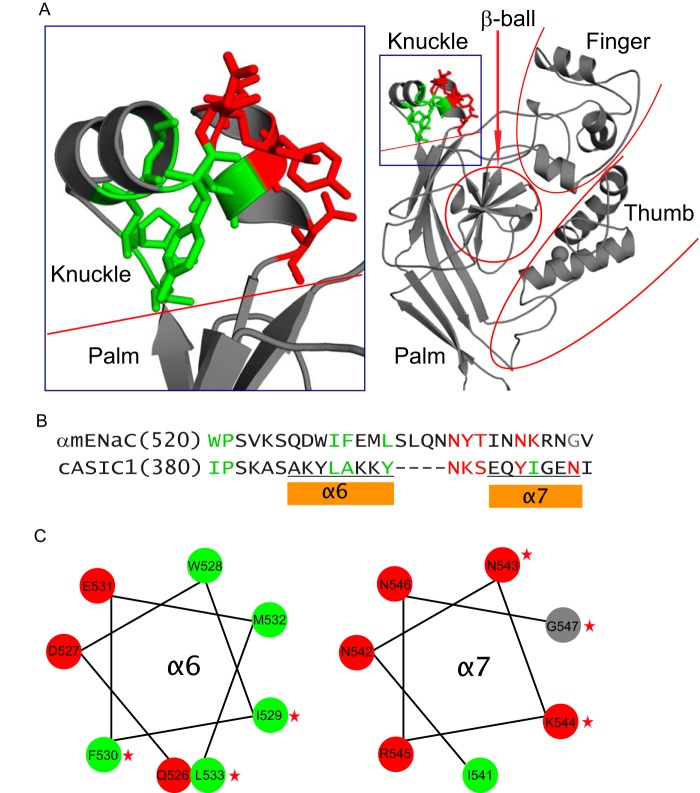
FIGURE 9.
α subunit knuckle domain residues mapped on the resolved ASIC1 structure. A, structural model for the extracellular region of an ASIC1 subunit (right) and the enlarged knuckle and upper palm domains (left). Sticks illustrate ASIC1 residues that are homologous to those of α subunit, where Cys substitutions greatly suppressed Na+ self-inhibition. Nonpolar residues are shown in green and polar residues in red. B, knuckle domain sequence alignments of the mouse α subunit and chicken ASIC1. As in A, sites in the α subunit where Cys substitutions greatly suppressed Na+ self-inhibition are shown in green (non-polar) or red (polar). A Gly residue is shown in gray. Tyrosine has both nonpolar (aromatic ring) and polar (hydroxyl group) features. Tyr393 of cASIC1 is shown in green because its nonpolar ring contacts other nonpolar residues. Tyr399 is shown in red because its polar hydroxyl group contacts polar side chains of other residues. C, α helical wheel projections of the α subunit knuckle domain α helices, indicated in B. Non-polar and polar residues are shown in green and red, respectively. The Gly residue is in gray. Stars identify residues where mutations significantly reduced Na+ self-inhibition.