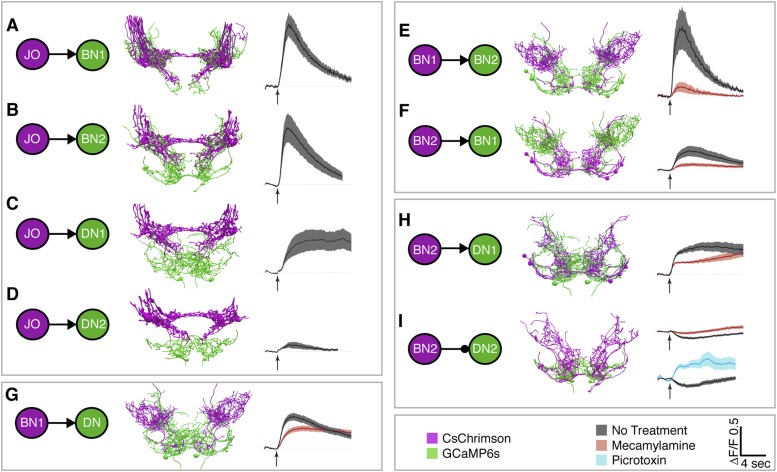
Figure 6. Different antennal grooming neurons are functionally connected.
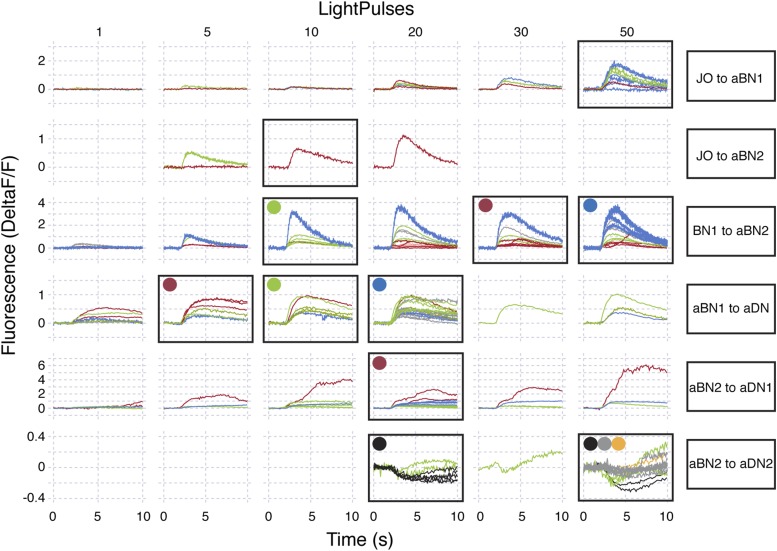
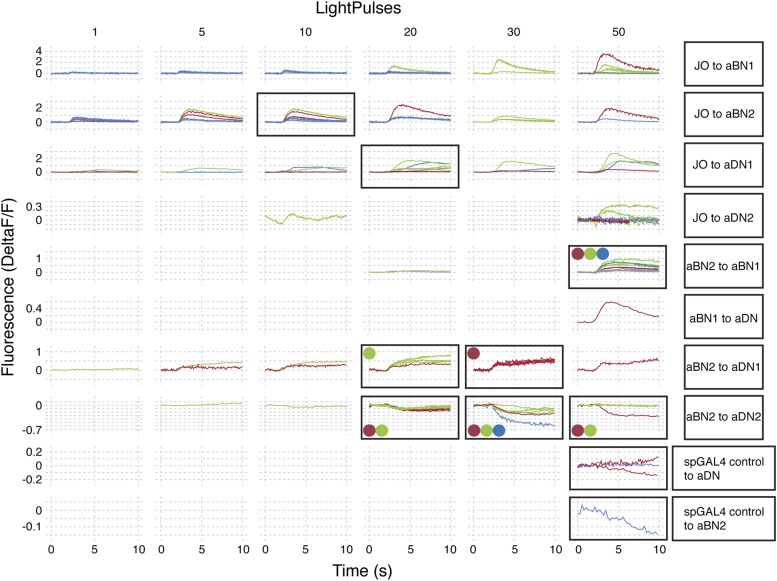
(A–I) Dissected CNSs with different neuronal classes expressing CsChrimson (magenta) were activated with red light while changes in calcium in their putative downstream partners expressing GCaMP6 (green) were imaged (ΔF/F). Each tested neuronal pair is shown using circles and as traced pairs. The direction of the connection and whether it is excitatory or inhibitory is depicted with an arrow (excitatory) or ball and stick (inhibitory). Changes in fluorescence of GCaMP6s of multiple flies under similar stimulus conditions are shown on the right (average ± s.e.m., 3–5 flies tested with 9–21 trials per trace). Arrow below each trace shows when the red light pulse was delivered. Black traces show flies that were imaged without drug treatment, whereas orange and blue traces were imaged while the nervous system was bathed with mecamylamine or picrotoxin respectively. See ‘Materials and methods’, Figure 6—figure supplement 1, Figure 6—figure supplement 2, Figure 6—figure supplement 3, and Supplementary file 2 for detailed ‘Materials and methods’, stimulus conditions, and controls. (A–D) aJO-LexA tested with the following interneuron spGAL4 pairs: (A) aBN1-spGAL4-1, (B) aBN2-spGAL4-1, (C) aDN1-spGAL4-1, and (D) aDN2-spGAL4-2. (E, F) aBN2-LexA tested with aBN1-spGAL4-1. (G) aBN1-spGAL4-1 tested with aDN-LexA. (H, I) aBN2-LexA tested with either (H) aDN1-spGAL4-1 or (I) aDN2-spGAL4-2.