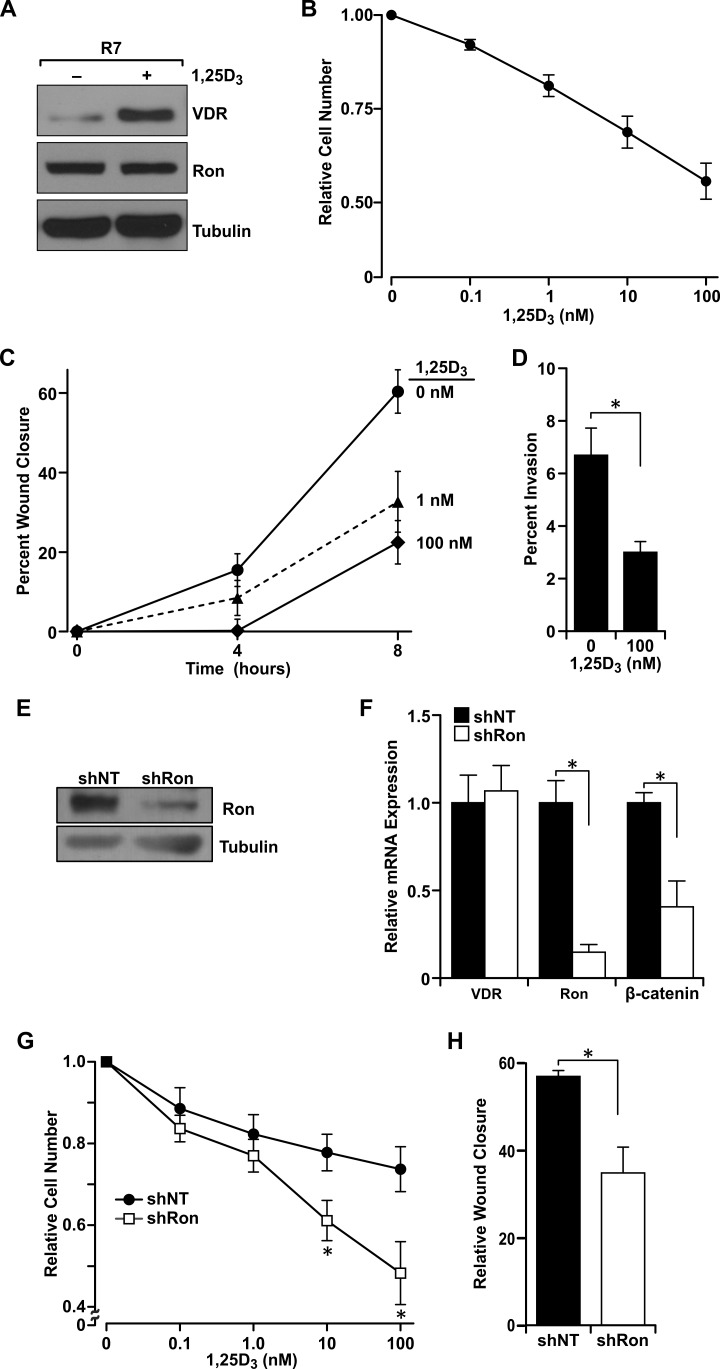
Figure 4. Ron receptor status determines epithelial cell sensitivity to vitamin D3-mediated growth inhibition and delays in migration and invasion.
A. Western analysis of levels of VDR and Ron ± 100 nM 1,25D3 in R7 cells. B. R7 cells were treated with the designated concentrations of 1,25D3 for 72 hours and cell viability/number was determined by crystal violet assays. Data are normalized to vehicle treated cells set at 1 and represent mean values from three independent experiments ± SE. C. R7 cells treated with the designated concentrations of 1,25D3 starting at the 0 hour time point were examined in scratch assays for the percent of gap closure after 4 and 8 hours. Data represent mean values from three independent experiments ± SE. D. Matrigel invasion assay with R7 cells in the presence or absence of 100 nM 1,25D3. Data represent mean values from four independent experiments ± SE. E. Western blot demonstrating the reduction in Ron expression in T47D cells stably transfected with a shRon lentivirus. F. qRT-PCR analysis of VDR, Ron and β-catenin mRNA expression in control T47D cells (shNT) and Ron knockdown T47D cells (shRon). Data represent mean values from three independent experiments ± SE. G. MTT assays of T47D control (shNT) and shRon cells treated with the designated concentrations of 1,25D3 for 48 hours. Data represent mean values from 3-4 independent experiments per cell line ± SE. H. Scratch assays in T47D control (shNT) and shRon cells treated with 100 nM 1,25D3 for 24 hours. Data represent mean values normalized to the vehicle-treated control group of each cell type and are from three independent experiments ± SE. *P < 0.05.