Figure 3.
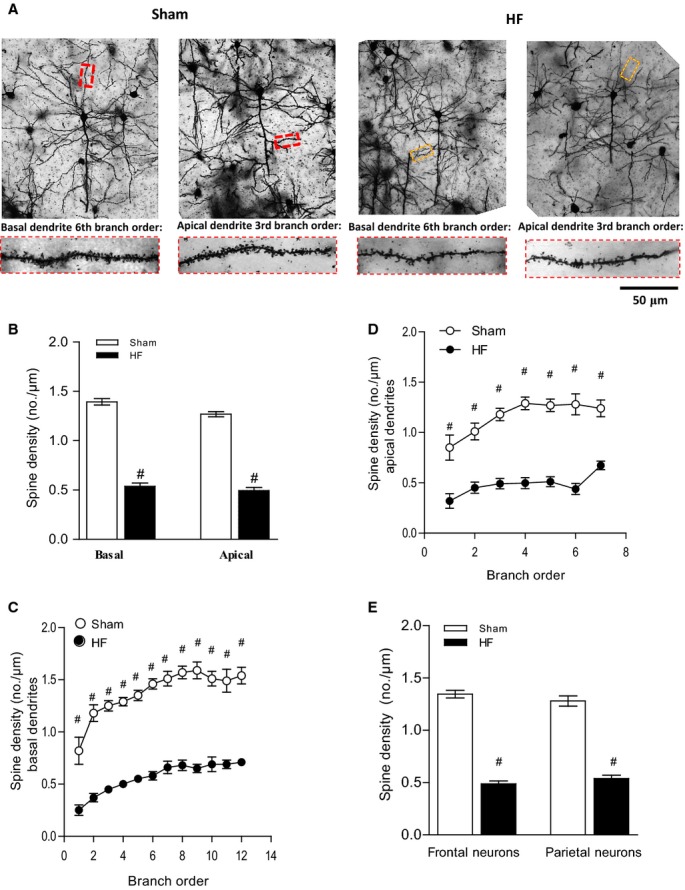
HF induces morphological changes and a reduction in number of dendritic spines. The sample population was composed of pyramidal cells chosen rostrocaudally from motor, sensory, and visual cortical regions (4 to 6 cells per animal). A, Depicts representative Golgi-stained images of cortical neurons of sham and HF wild-type mice and illustrates the differences between the basal and apical neurons of sham mice, which had significant more dendritic branches and thicker branch diameters than those of HF mice. The magnification shows details of both basal and apical dendrite morphology. B, Spine density of both basal and apical dendrites was reduced in the frontal cortex in HF mice. Breakdown analysis (dendrograms) further revealed a significant loss of spines or spine density in both (C) basal and (D) apical dendrites of HF compared with sham. E, Spine density of frontal neurons and parietal neurons is significantly reduced during HF. For all tasks: sham n=18, HF n=20, #P<0.001. HF indicates heart failure.
