Fig. 3.
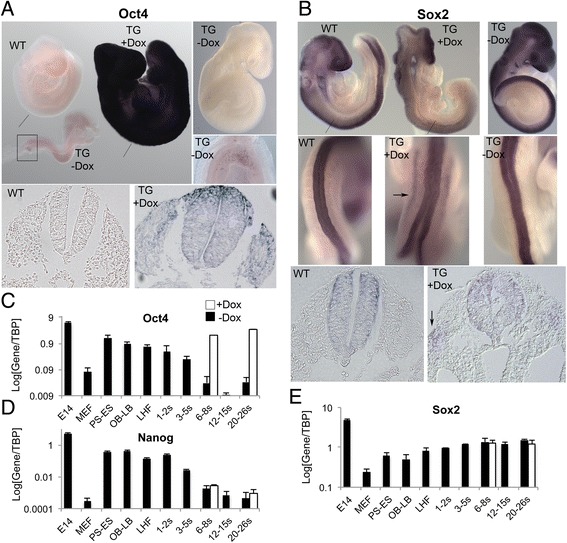
Induction of ubiquitous ectopic Oct4 expression. a Top: Oct4 mRNA expression in wild type (wt) and induced (+Dox) or un-induced (−Dox) TgOct4 transgenic (TG) somitogenesis embryos analysed by whole mount in situ hybridisation. A high magnification image of Oct4 expression in the PGCs of the transgenic, un-induced E8.5 embryo is also shown on the right corresponding to the boxed area. Bottom: representative sections showing Oct4 expression in the wild type (left) and the induced transgenic (right) embryos. The position of the sections relative to the embryo is indicated by the lines on the top left image. b Top: Sox2 mRNA expression in wild type (wt) and induced (+Dox) or un-induced (−Dox) TgOct4 transgenic (TG) somitogenesis embryos analysed by whole mount in situ hybridisation. Middle: High magnification images depicting Sox2 expression in the neural tube. Arrow: Ectopic lateral Sox2 expression in induced embryo. Bottom: representative sections showing Sox2 expression in the wild type (left) and the induced transgenic (right) embryos. The position of the sections relative to the embryo is indicated by the lines on the top left image. Arrow: Ectopic Sox2 expression in induced embryo. c-e Log expression levels of Oct4, Nanog and Sox2 in pooled pre- and somitogenesis stage TgOct4 embryos in the presence (white bars) or absence of Doxycycline (black bars). Error bars represent s.e.m. (n = 3). Note error bars in (c) are smaller than the resolution of the figure. In all cases Oct4-induced embryos were treated with Doxycycline for 24 h prior to the indicated recovery time point. E14, E14tg2a ES cells; MEF, mouse embryonic fibroblasts; PS, prestreak; ES, early streak; OB, no allantoic bud; LB, late allantoic bud; LHF, late headfold; s, somite
