Fig. 6.
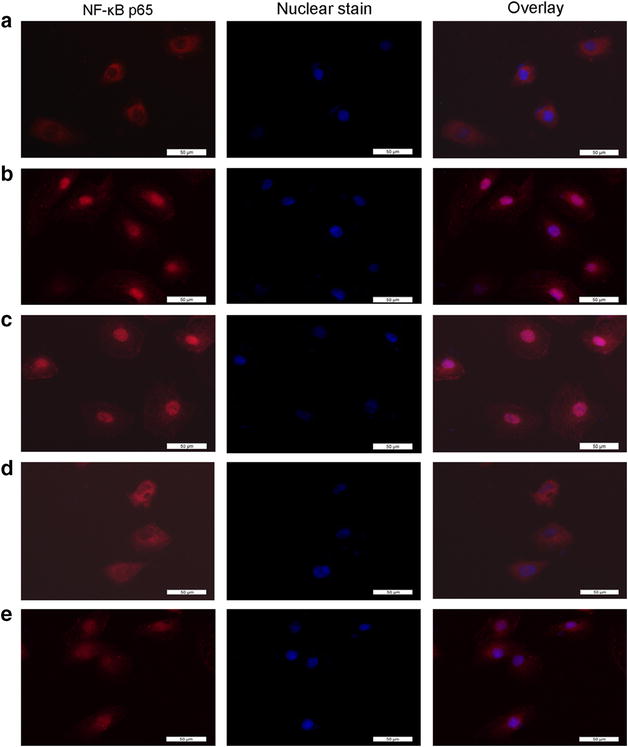
Immunofluorescence images of p65 nuclear translocation under the fluorescence microscopy. Red fluorescence indicates localization of NF-κB p65. Cofilinl knockdown suppressed AngII-induced nuclear translocation and activation of NF-κB: a without AngII stimulation NF-κB was predominately found in the cytoplasm. b With AngII stimulation, NF-κB translocated into the nucleus. c Transfection with nonspecific control lentiviruses had no effect on AngII-induced NF-κB translocation, as there were still obviously p65 staining in the nuclei. d Transfection with lentiviruses containing cofilin1 shRNA evidently inhibited the AngII-induced NF-κB translocation, as there was only a little of nuclear p65 staining found. e GSPE pretreatment inhibited AngII-induced NF-κB translocation. Magnification ×400. Scale bar represents 50 μm
