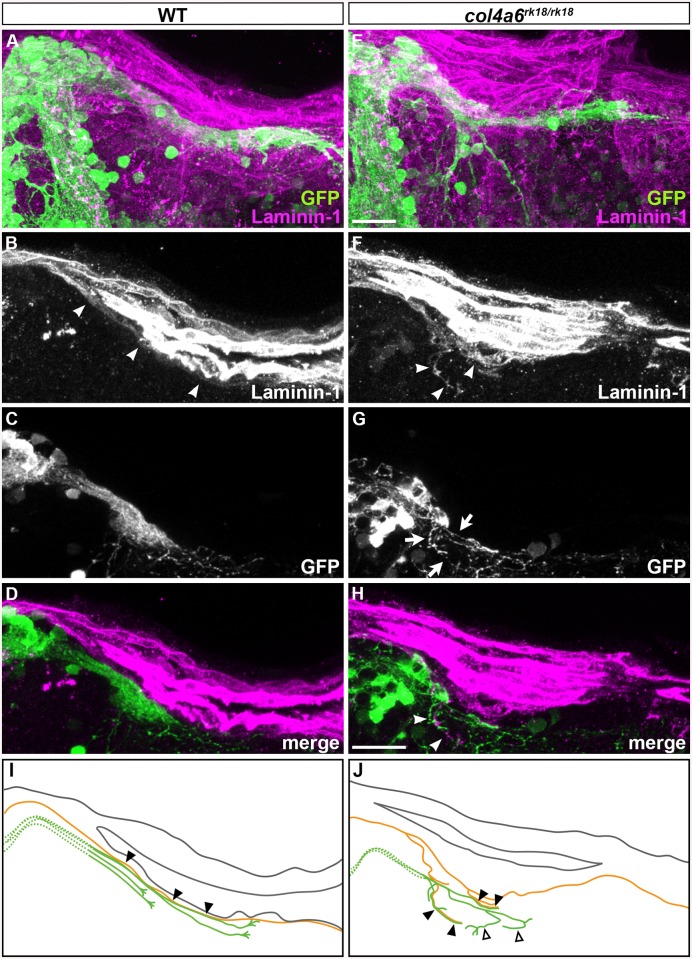
Fig 7. Abnormal BM structure is coupled with the abnormal axogenesis of GCs in col4a6 mutants.
Wild-type (A-D) and col4a6 mutant (E-H) transgenic larvae that express GFP in the GC (hspGFFDMC90A; UAS:GFP) were stained at 5 dpf with anti-GFP (green) and anti-laminin–1 (magenta) antibodies. Dorsal projection views (A, E); 9.723-μm-thick projection views (B-D, F-H). (I, J) Schematic representation of BM (brown) and GC axons (green) in wild-type (A-D) and the col4a6 mutant (E-H) hindbrain. The laminin–1+ BM structure was split into two layers in the col4a6 mutant (indicated by arrows in G). In the same region, the corresponding GC axons were bifurcated, some of the axons ran along the split BM layers (indicated by arrowheads in F and H, by closed triangles in J) and some of them did not run along the BM layer (indicated by open triangles in J). The root of the GC axons cannot be distinguished from one another and thus is described by a dotted line. Scale bars: 20 μm in E (applied to A); 20 μm in H (applied to B, C, D, F, G).