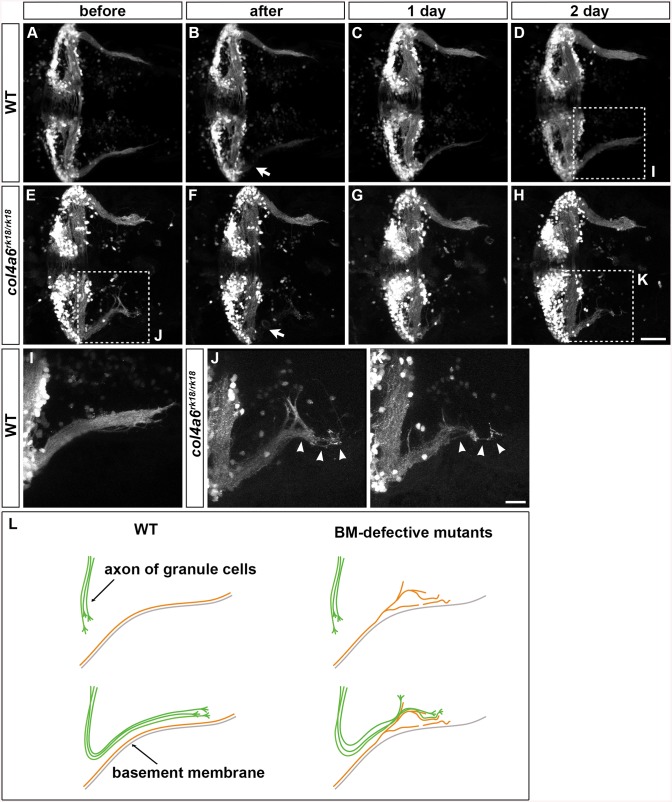
Fig 8. Abnormality in regenerating GC axons is linked to the abnormal BM structure in col4a6 mutants.
The axons of caudolateral GCs in wild-type and col4a6 mutant larvae harboring the hspGFFDMC90A (GC-specific Gal4) and UAS:GFP transgenes were ablated by a laser on the left side (marked by arrows) at 5 dpf. The GC axons of the larvae were observed before (A, E), soon after (B, F), or 1 (C, G) or 2 days (D, H) after the laser ablation. Dorsal views of the rostral hindbrain regions. (I, J, K) High-magnification images of boxes I (in D), J (in E), and K (in H). Some of the regenerated axons followed the same abnormal routes that were used by the original axons in the col4a6 mutant (indicated by arrowheads in J and K). (L) Schematic representation of the axogenesis of caudolateral GCs in wild-type and BM mutant (col4a5 and col4a6) larvae. Scale bars: 50 μm in H (applied to A-G); 20 μm in K (applied to I, J). (See more examples in S5 Fig).