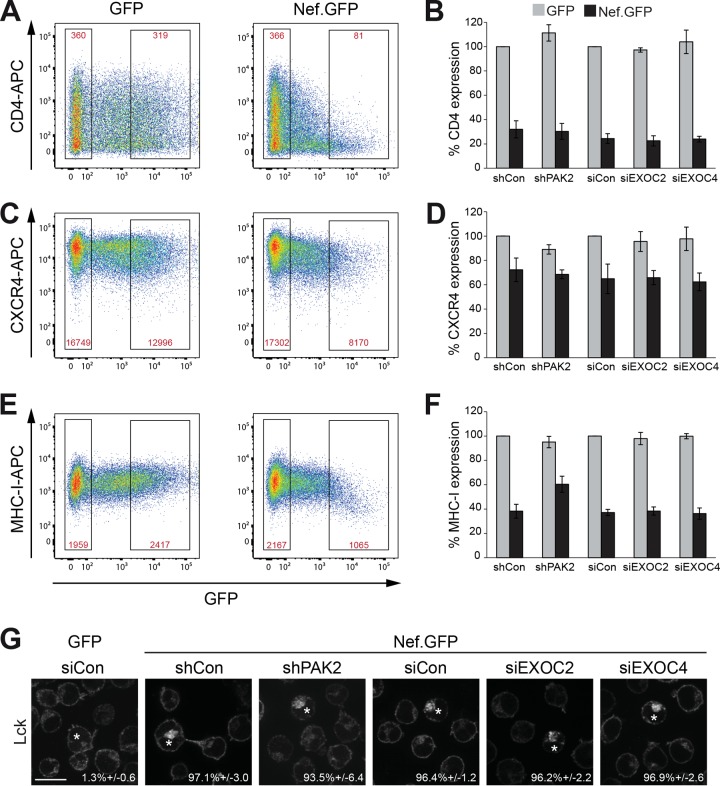
FIG 4 .
EXOC does not affect Nef-mediated perturbations of host cell vesicular transport. (A) Cell surface CD4 levels. Jurkat T (CCR7) lymphocytes transiently expressing GFP or SF2 Nef.GFP were stained with allophycocyanin (APC)-conjugated antibodies against CD4 and analyzed by flow cytometry. Gates of live nontransfected and highly expressing cells are indicated. Red values are the mean fluorescence intensities of the CD4 signals in the respective gates. (B) Quantification of relative CD4 cell surface levels as shown in panel A. Mean fluorescence intensity percentages of highly expressing and nontransfected cells treated with shRNA or siRNA, as indicated, were calculated relative to the corresponding GFP control, which was set to 100%. Displayed are the mean values ± the standard deviations from three independent experiments. (C and D) Cell surface CXCR4 levels. Primary fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) plots (C) and quantification (D) of cell surface CXCR4 levels as detected by APC-conjugated antibodies to CXCR4. (E and F) Cell surface MHC-I levels. Primary FACS plots (E) and quantification (F) of cell surface MHC-I levels as detected by APC-conjugated antibodies to MHC-I. (G) Representative confocal micrographs of Jurkat T (TAg) lymphocytes expressing GFP or Nef.GFP in the context of shRNA-mediated depletion of PAK2, siRNA-mediated reduction of EXOC2 or EXOC4, or the respective control. Cells were plated onto coverslips, fixed, permeabilized, and stained for endogenous Lck, which accumulates in the TGN in the presence of Nef. Asterisks designate GFP-positive cells. Values are the mean percentages ± the standard deviations of cells with intracellular Lck accumulation from three independent experiments. Scale bar, 10 µm. For dual-color images, see Fig. S4C in the supplemental material.