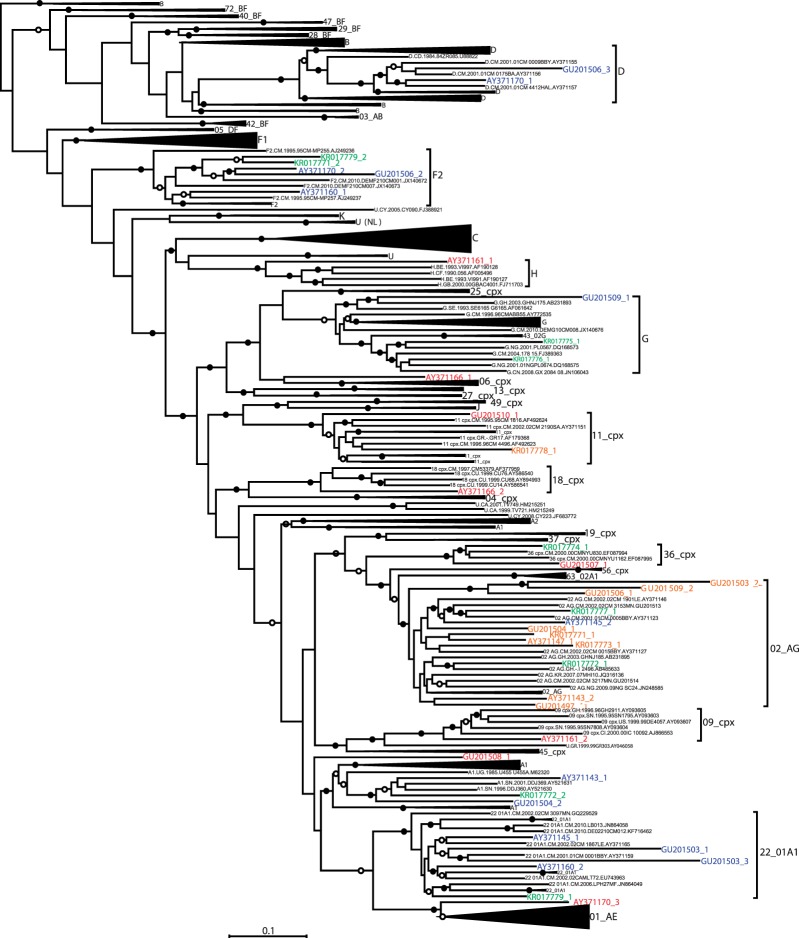
Figure 3.
Maximum likelihood tree indicating the phylogenetic placement of recombinationally derived genome fragments drawn from 22 Cameroonian URF sequences in relation to a representative selection of near full-length sequences selected from amongst all published subtype, CRF and unclassified sequences available in the LANL database (http://hiv-web.lanl.gov/content/hiv-db) in June 2014. Some of the clades were collapsed for the sake of clarity. A version of the tree with uncollapsed clades is available on request. The tree was constructed with 500 full ML bootstrap replicates using RAxML. Solid and open circles indicate branches with >70 and 50% bootstrap support, respectively. The tree was midpoint rooted. Orange segments represent divergent sequences residing very near the base of branches of subtrees containing previously defined HIV-1 subtype or CRF lineages whereas red sequences represent divergent sequences residing on isolated branches outside of subtrees containing previously defined HIV-1 subtype or CRF lineages. Green and blue sequences represent recombinationally derived sequence fragments respectively drawn from the newly characterised and previously described Cameroonian URFs that are embedded within well characterised subtype and CRF clades