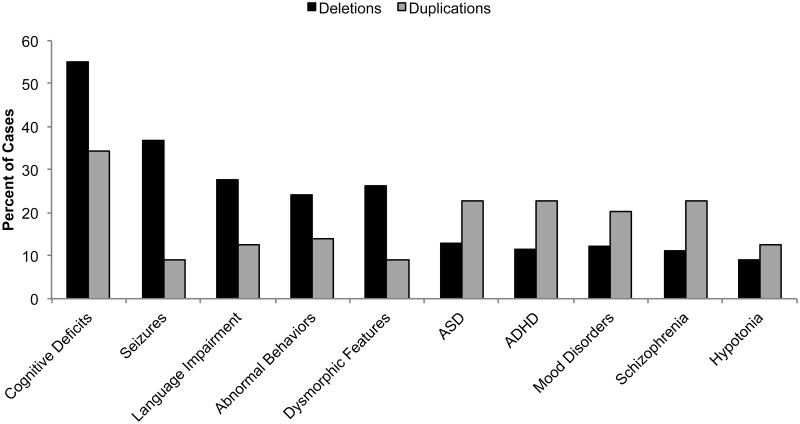
Figure 4. Clinical features of individuals with heterozygous CHRNA7 CNVs.
Cognitive deficits were the most prevalent phenotype in both duplication and deletion patients. Seizures (including epilepsy and EEG abnormalities) were considerably more common in patients with CHRNA7 deletions. ASD, ADHD or attention difficulties, mood disorders, and schizophrenia were more common in individuals with CHRNA7 duplications. Cognitive deficits (including ID, DD, and learning difficulties) were the only features to occur in near half of all individuals with heterozygous CNVs, emphasizing the variable expressivity associated with CHRNA7 changes in copy number. Mood disorders includes anxiety, bipolar disorder, depression, and unspecified mood disorders. Phenotypically normal individuals, homozygous deletions and triplications not included.