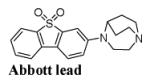
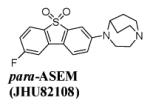
Table 1.
Inhibition in vitro binding affinities (Ki, nM) of ASEM, para-ASEM and the Abbott lead toward α7-nAChR, heteromeric nAChR subtypes and 5-HT3 [48].
| Compound | α7-nAChR a | Heteromeric nAChR subtypes b | 5-HT3c | Selectivity | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α2β2 | α2β4 | α3β2 | α3β4 | α4β2 | α4β4 | α7/α4β2 | α7/5HT3 | |||
|
0.3, 0.5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 660d | - | - |

|
0.37, 0.45 | >10000 | 4000 | 1000 | 709 | 562 | 1000 | 230 | 1370 | 561 |
|
1.32, 1.35 | 1000 | 8000 | 2000 | 5000 | 885 | 3000 | 505 | 663 | 378 |
Rat cortical membranes, radiotracer [125I]α-bungarotoxin (0.1 nM), KD = 0.7 nM
Inhibition in vitro binding assay of all heteromeric nAChR subtypes was performed with stably transfected HEK293 cells and [3H]epibatidine (0.5 nM), KD = 0.021 nM (α2β2-nAChR), KD = 0.084 nM (α2β4-nAChR), KD = 0.034 nM (α3β2-nAChR), KD = 0.29 nM (α3β4-nAChR), KD = 0.046 nM (α4β2-nAChR), KD = 0.094 nM (α4β4-nAChR).[80]
Human 5-HT3 recombinant/HEK293 cells, radiotracer [3H]GR65630 (0.35 nM), KD = 0.5 nM
the Ki value is taken from[60]
