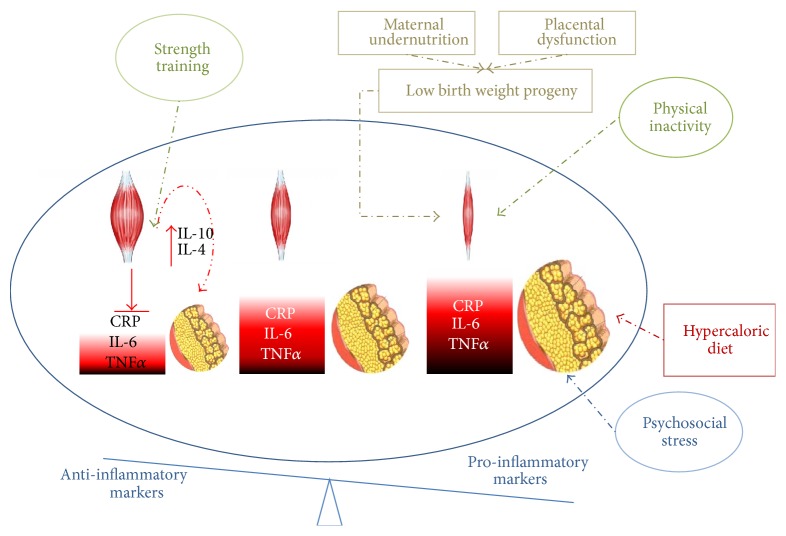
Figure 1.
The opposing influences of muscle mass and fat mass on the pro-inflammatory : anti-inflammatory balance. The middle condition shows normal muscle mass and fat mass. The condition on the right shows the impact of low birth weight and lower muscle mass/strength interacting with lifestyle influences such as inactivity, which also promotes lower muscle mass/strength and hypercaloric diets, promoting increased fat mass. Larger fat mass stimulates pro-inflammatory adipokine release and reduces anti-inflammatory adipokine release, while lower muscle mass/strength and lower physical activity are associated with higher pro-inflammatory adipokine and lower anti-inflammatory myokine release, respectively. To the left is the condition whereby the influence of strength training stimulates muscle mass/strength, associated with a lower inflammatory burden and which also promotes the secretion of anti-inflammatory myokines such as IL-4 and IL-10.