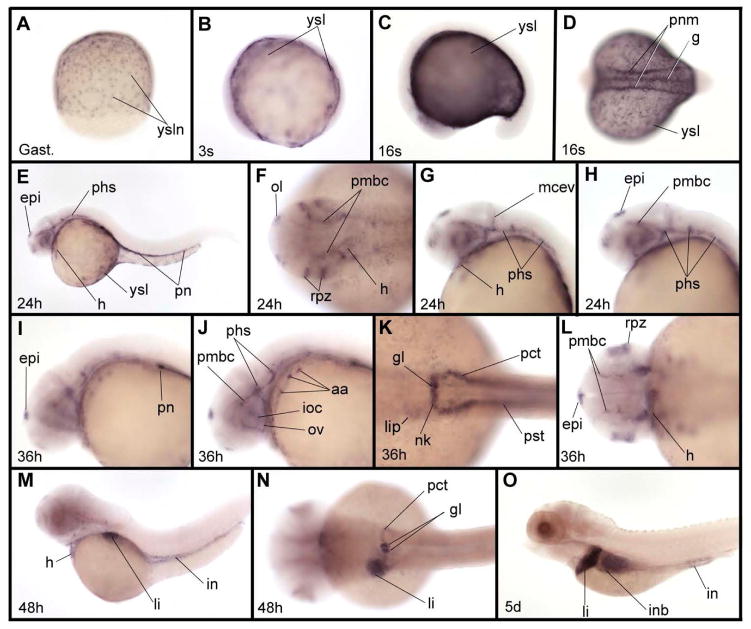
Fig. 3.
Expression pattern of zIQGAP2 mRNA during embryonic and larval development. (A) zIQGAP2 transcripts accumulate in nuclei of the yolk syncytial layer (ysl) at gastrula stage (Gast.). (B) At early somitogenesis (3-somite stage, or 3s) expression is observed in the whole ysl. (C, D) At the middle of somitogenesis (16-somite stage, or 16s) transcripts were found in the ysl, gut and pronephric mesoderm (pnm). (E–H) At 24 hpf (24h) additional expression is found in the epiphysis (epi), heart (h), olfactory vesicles (ol), retina proliferative zone (rpz), and a subpopulation of cephalic blood vessels that includes the primary head sinus (phs), middle cerebral vein (mcev) and primordial midbrain channel (pmbc). In the trunk, expression is observed in the pronephros (pn). (I–L) At 36 hpf (36h) additional expression in cephalic blood vessels were observed in aortic arches (aa), optic artery (ov) and inner optic circle (ioc). In trunk, expression is observed in all derivatives of the pronephric mesoderm, including the glomeruli (g), neck (nk), proximal convoluted tubule (pct) and proximal straight tubule (pst). Expression in the epiphysis shown in (L) is much stronger on the left side. (M, N) At 48 hpf (48h) zIQGAP2 transcripts were observed in heart, liver (li) and intestine (in), as well as in pronephros tissues, including glomeruli, neck and proximal convoluted tubule. (O) At 5 dpf (5d) transcripts were observed in pronephros, liver, intestinal bulb (inb) and intestine. Embryos were shown anterior to the left and dorsal to the top in lateral views (C, E, G–J, M, O), and anterior to the left in dorsal views (B, D, F, K–L, N). Embryo in A is in dorsal view, animal pole to the top.