Fig. 5.
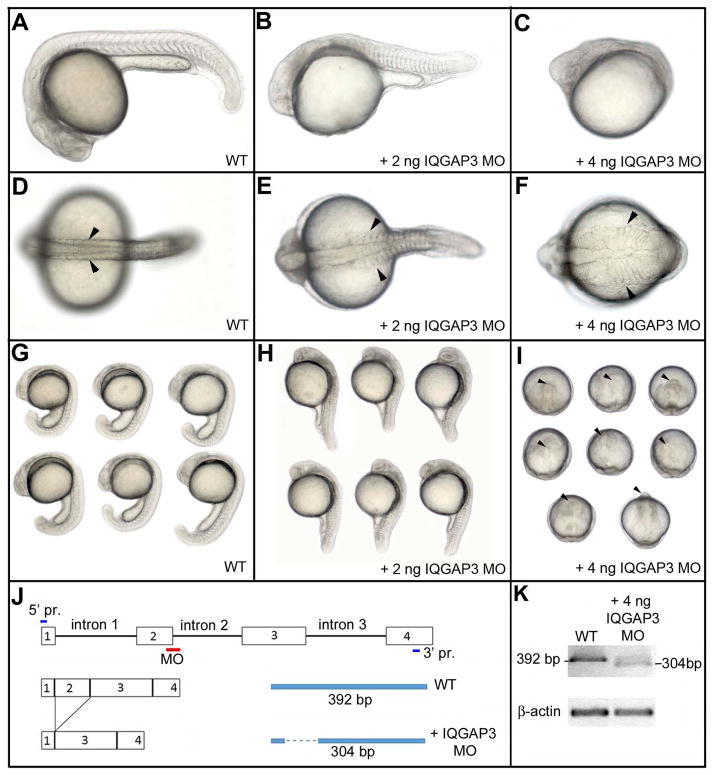
zIQGAP3 MO knockdown phenotypes. At 24hpf, compared to WT (A, D, G), zIQGAP3 morphant embryos obtained by injection of 2 ng (B, E, H; n = 271) or 4 ng (C, F, I; n = 350) of zIQGAP3 MO display a wider (arrowheads) and posteriorly truncated embryonic axis. To prevent cell death resulting from P53 activation (Robu et al. 2007) 4 ng of P53 MO was coinjected with IQGAP3 MO. Arrowheads in I indicate the anterior tip of the embryonic axis. Embryos are in lateral (A–C, G, H) or dorsal view (D–F), with anterior to the left. Groups of embryos (G–I) are in lateral (G, H) or dorsal view (I), with anterior on the top. (J) Schematic presenting the binding site of zIQGAP3 MO and its interfering mechanism by removing exon 2 of zIQGAP3 pre-mRNA. (K) WT and truncated pre-mRNA covering first four exons were amplified by RT-PCR and analyzed to confirm the interfered splicing of zIQGAP3 mRNA. Notice the loss of WT mRNA band and the appearance of a smaller band representing the truncated mRNA (which lacks exon 2 due to MO-driven splicing interference).