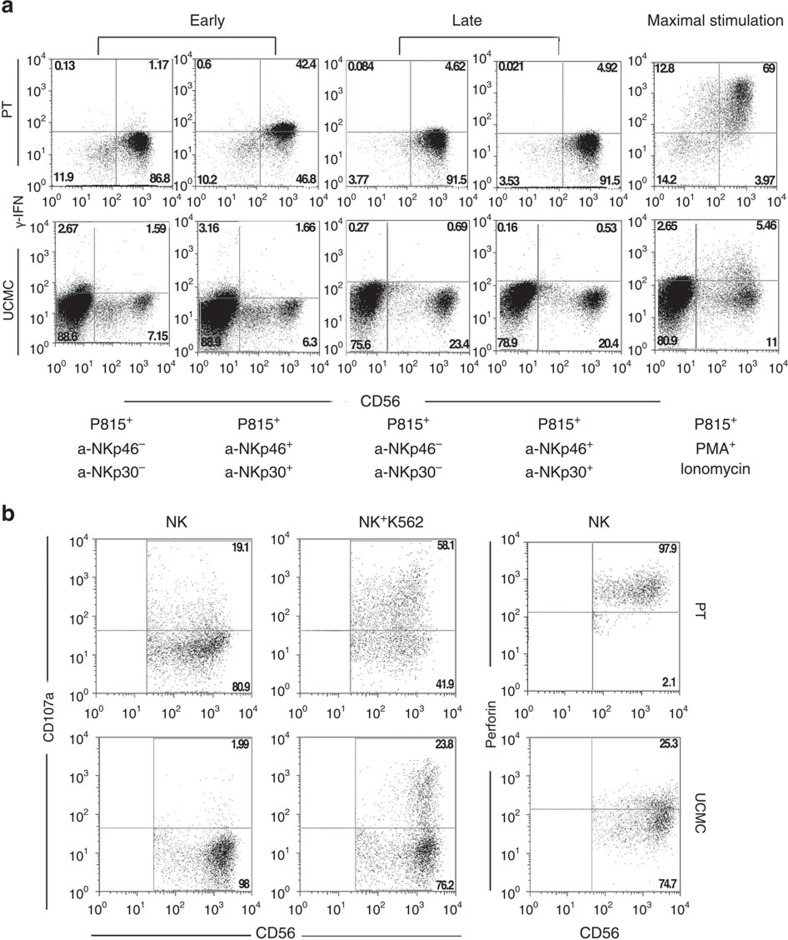
Figure 5. Functional characterization of immature NK cells derived from Lin−CD34+DNAM-1bright PBMC.
(a) IFNγ production by CD34-derived NK cells. Flow cytometric detection of IFNγ−producing NK cells growing in vitro from either purified patient peripheral blood DNAM-1brightCD34+ PBMC (PT) or from cord blood DNAM-1negCD34+ cells. IFNγ production was evaluated after stimulation as occurring early (0–16 h) and late (16/20–24 h) stimulation31. Representative of 10 experiments. (b) Flow cytometric CD107a degranulation assay and perforin expression in NK cells derived in vitro from purified DNAM-1brightCD34+ HIV-PBMC and from purified DNAM-1negCD34+ UCMC. NK-cell effectors were challenged with K562 target cells at 5:1 E/T ratio for 4 h. CD107a expression was detected on CD56+CD3−CD33−-gated cells (middle panel). Left panel: no target negative control. Right panel: intracytoplasmic perforin in NK cells derived from patient-purified CD34+DNAM-1bright cells (PT) and from uninfected cord blood-derived CD34+ cells (UCMC) after 20 days of in vitro culture. Representative of 10 experiments.