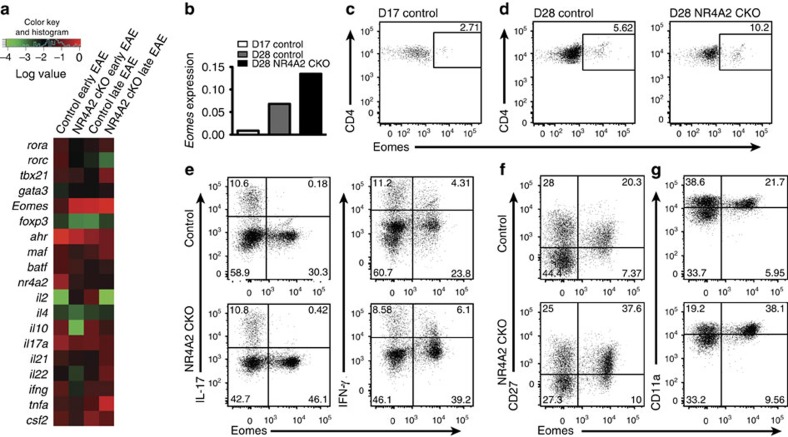
Figure 2. Late/chronic EAE is associated with Eomes expression by pathogenic CNS-infiltrating CD4+ T cells.
(a) Differential expression of immune-associated genes. CD4+ T cells were isolated and sorted from control and NR4A2 cKO CNS from mice with early or late EAE, and analysed by expression microarray. Gene expression was confirmed by quantitative reverse transcriptase–PCR (qRT–PCR) and relative expressions of selected genes are summarized by heat map. (b) Differential expression of eomes in the CNS CD4+ T cells determined by qRT-PCR. (c,d) Intracellular flow cytometry for Eomes expression of freshly isolated CNS T cells. Unstimulated cells were stained intracellularly. (e–g) Flow cytometric analyses for co-expression of IL-17, IFN-γ, CD27 and CD11a, with Eomes in CD4+ CNS-infiltrating T cells (Day 27). The cells were stained after stimulation with PMA/ionomycin in the presence of GolgiPlug for 5 h. FACS staining plots are representative of at least three independent EAE experiments.