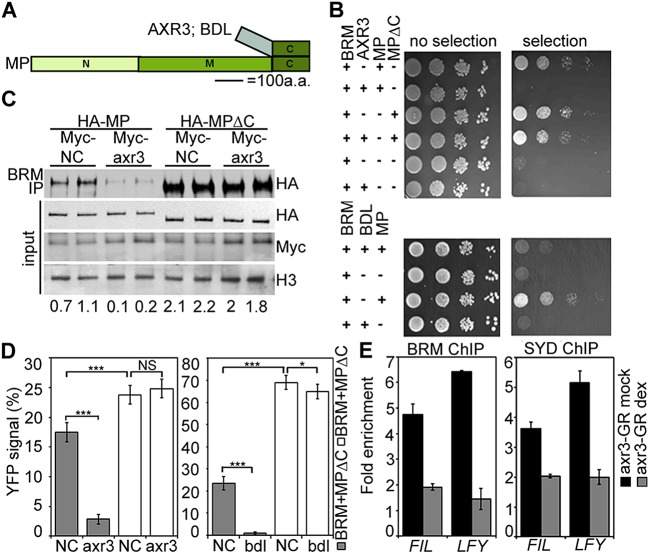
Figure 7. Aux/IAA proteins prevent BRM and SYD recruitment by MP.
(A) Diagram of MP domains. N: N-terminal DNA binding/dimerization domain, M: middle BRM/SYD interacting region, C: C-terminal Aux/IAA interacting domain. (B) Yeast-three-hybrid test of BRM interaction with MP or MP lacking the C-terminal domain (MP∆C) in the presence of the Aux/IAA protein AXR3 (top) or BDL (bottom). Growth was assayed with (right) or without (left) 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole. (C) Co-immunoprecipitation of FLAG-BRM with HA-MP or HA-MP∆C in the presence of the stabilized Myc-axr3. NC: Myc-tagged unrelated protein of similar molecular mass as axr3. Below: Amount of precipitated HA-MP/HA-MP∆C (% input). (D) Quantification of BiFC test of interaction between BRM and MP or BRM and MP∆C in the presence of axr3 (left) or bdl (right) compared to a NC protein. The error bars are proportional to the standard error of the pooled percentage computed using binomial distribution. n = 3. p-value: Mann–Whitney U test. (E) ChIP to assess BRM and SYD association with MP target gene loci before (mock) or after (dex) nuclear entry of axr3-GR. Shown is fold-enrichment relative to a control locus (Ta3 retrotransposon).