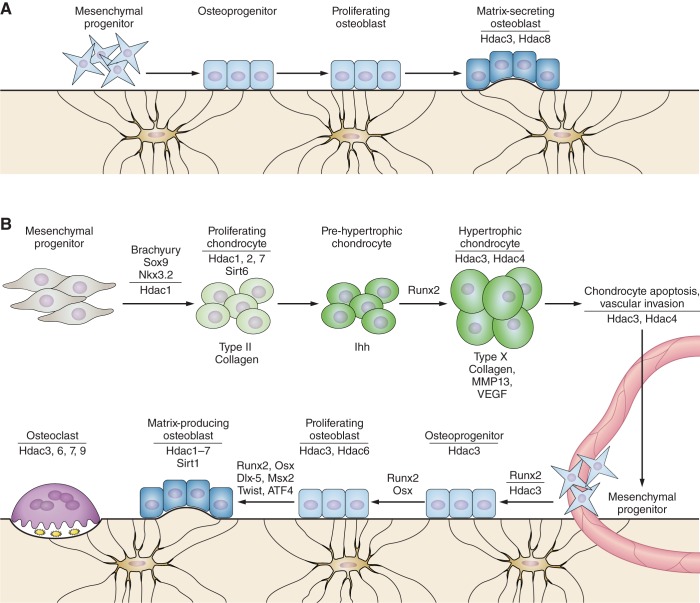
Figure 2.
Hdacs in bone and cartilage development. A: Hdacs facilitate intramembranous bone ossification. Mesenchymal cells differentiate directly into osteoblasts during intramembranous bone formation. Deletion of Hdac3 or Hdac8 within the developing skeleton alters intramembranous ossification, skull formation, and bone density. B: during endochondral ossification, mesenchymal condensations give rise to a cartilaginous template for bone formation. Several Hdacs regulate chondrogenesis in the sclerotome, the expression of matrix genes associated with chondrocyte proliferation, and hypertrophy. Hdacs control bone modeling by influencing osteoblast commitment, promoting osteoblast proliferation, regulating osteoblast maturation and matrix deposition, and by facilitating osteoclast resorption activity and motility.