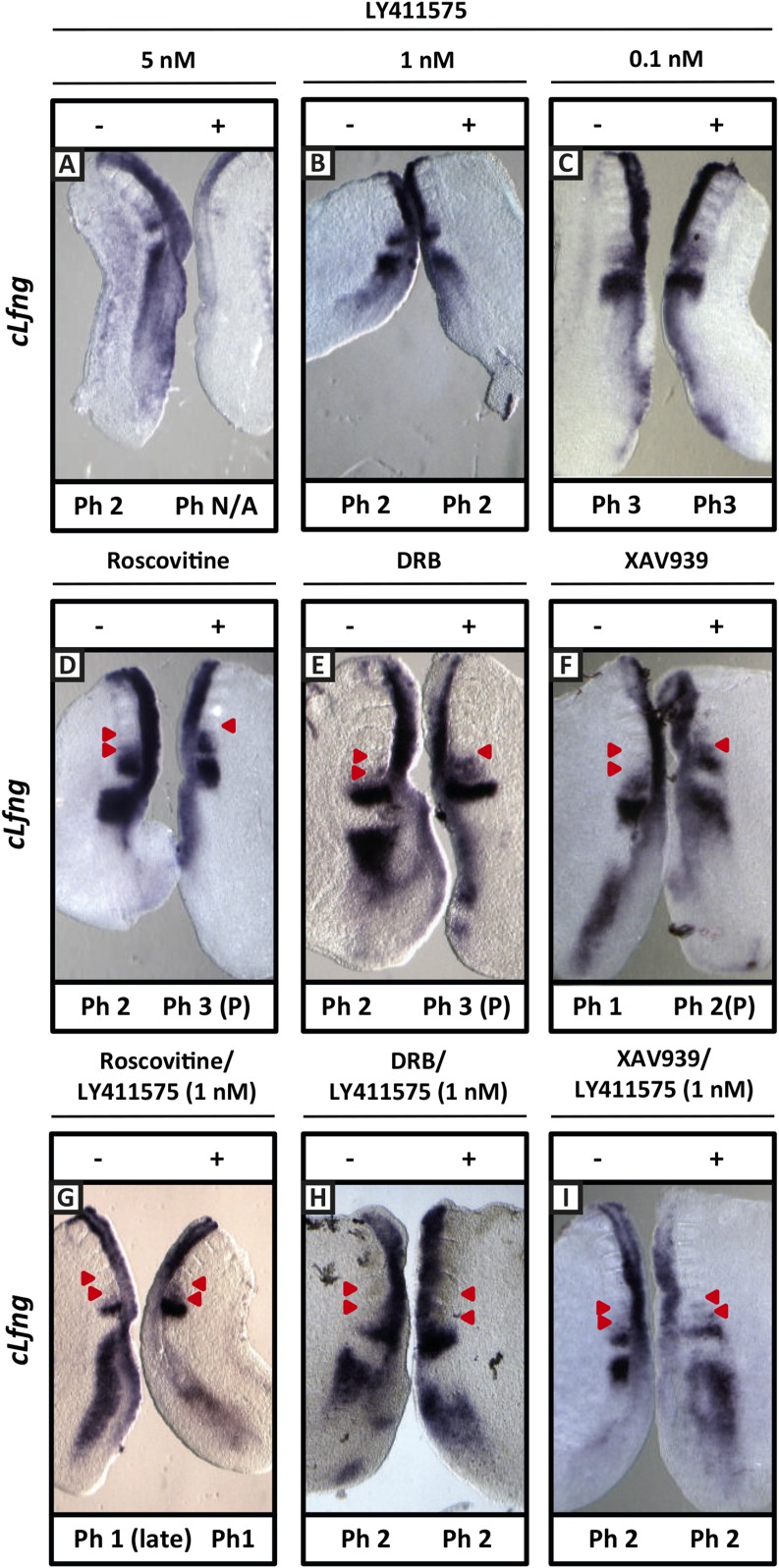
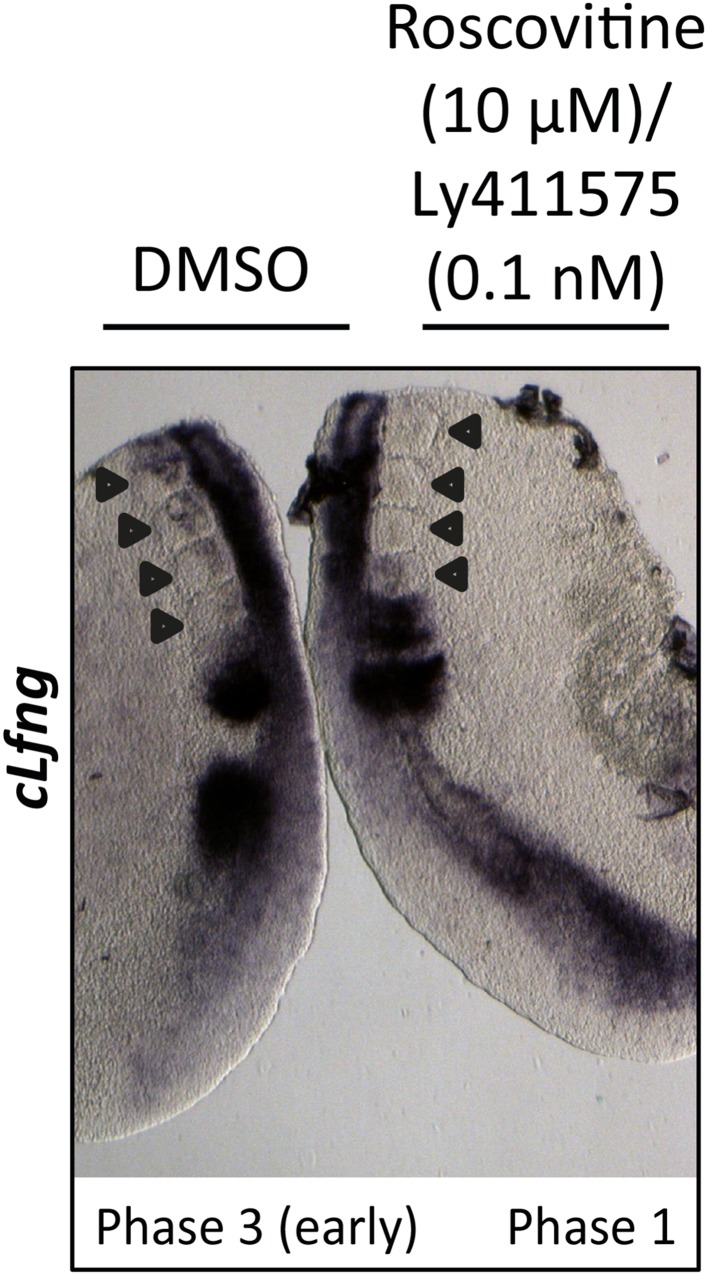
Figure 8. Exposure to 1 nM LY411575 rescues the delay in clock gene oscillations caused by Roscovitine, DRB and XAV939.
Bissected chick or mouse caudal explant pairs treated ‘−’ or ‘+’ inhibitor and then analysed by insitu hybridisation for Lfng mRNA expression: (A–C) Treatment of chick PSM explants in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 5 nM LY411575 (A), 1 nM LY411575 (B), 0.1 nM LY411575 (C) for 3 hr reveals that 5 nM LY411575 severely downregulates cLfng expression whereas 1 nM and 0.1 nM do not appear to change levels or domain of cLfng expression. (D–F): Treatment of chick PSM explants in the presence (+) or absence (−) of Roscovitine (D), DRB (E) or XAV939 (F) for 3 hr reveals that ‘+’ explants have lagging expression of cLfng, with one less somite formed than the ‘−’ explants. (G–I): Treatment of chick PSM explants in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 1 nM LY411575 together with Roscovitine (G), DRB (H) or XAV939 (I) for 3 hr reveals that 1 nM LY411575 rescues the delay in clock gene oscillations caused by these three inhibitors such that the cLfng expression domains in the ‘−’ and ‘+’ explants are very similar. The red arrowheads identify the somites formed during the in vitro culture period of the assay. (P) = previous cycle.