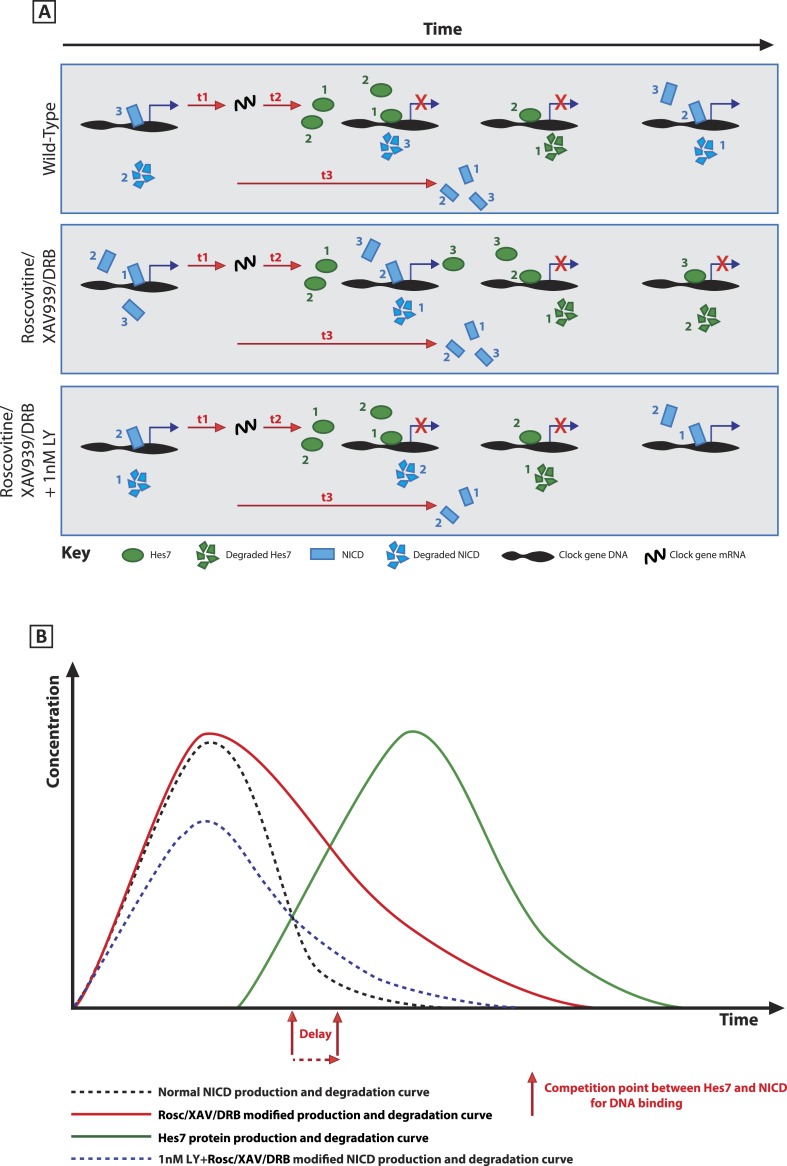
Figure 9. A schematic illustration depicting how modification of NICD stability may cause a delay to the period of the oscillations.
(A) Schematic showing the competition between molecules of Hes7 and NICD for binding to the promoter of a clock gene. Exposure to Roscovitine, XAV939 or DRB causes increased stability and levels of NICD and thus NICD occupies the promoter for longer than in the wild-type situation, thereby prolonging the oscillation period. Exposure to 1 nM LY411575 together with Roscovitine, XAV939 or DRB reduces the level of NICD production offsetting the increased stability which rescues the delay. t1 = delay due to transcription of Hes7 and Notch; t2 = the delay due to translation of Hes7; t3 = delay due to translation of Notch and subsequent ligand dependent production of NICD. (B) Graphical model depicting how modifying the stability of NICD may cause a delay to the period of the oscillations by delaying the time-point at which proportional levels of NICD and Hes7 allow switching of promoter occupancy of these two factors.