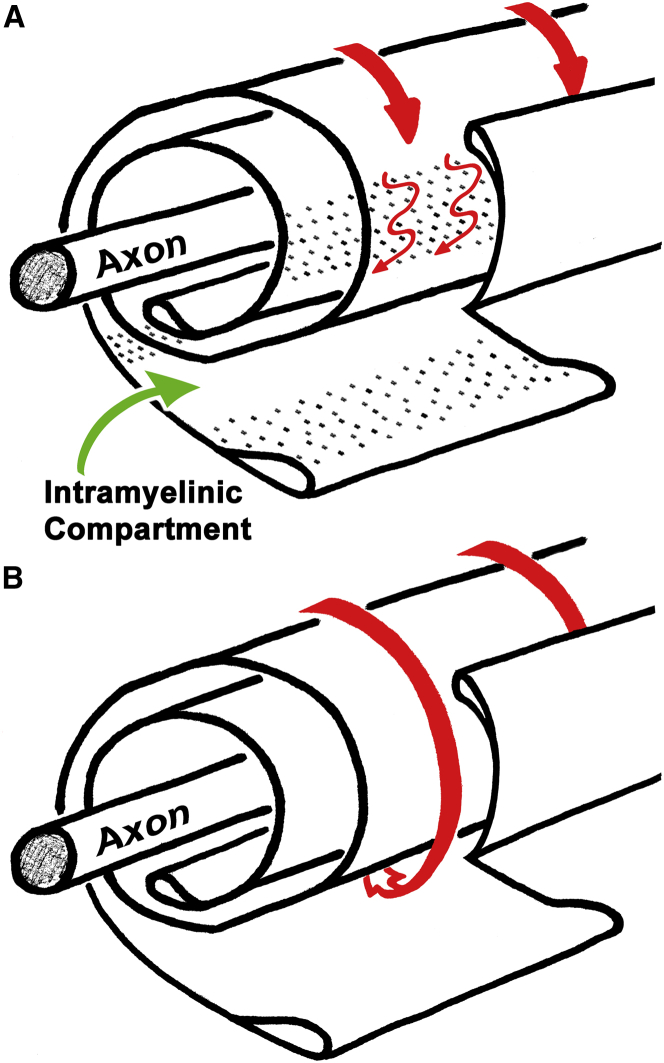
Figure 7.
Claudin-11 TJs form a diffusion barrier in CNS myelin. (A) When a spiral of normal, multilayered CNS myelin is unraveled, claudin-11 TJs (dots) can be observed in the intramyelinic compartment. These TJs typically extend though the entire thickness of the sheath and, in mature myelin, are enriched in the region of the sheath between the inner and outer mesaxons. In the presence of these TJs, which span the intramyelinic compartment, this space is partially occluded, and diffusion (red arrows) through this space is obstructed. (B) In Cldn11-null tissue, myelin ultrastructure is unaltered, but CNS myelin TJs are absent. In the absence of these TJs, the intramyelinic compartment is more accessible, and diffusion occurs more rapidly. To see this figure in color, go online.