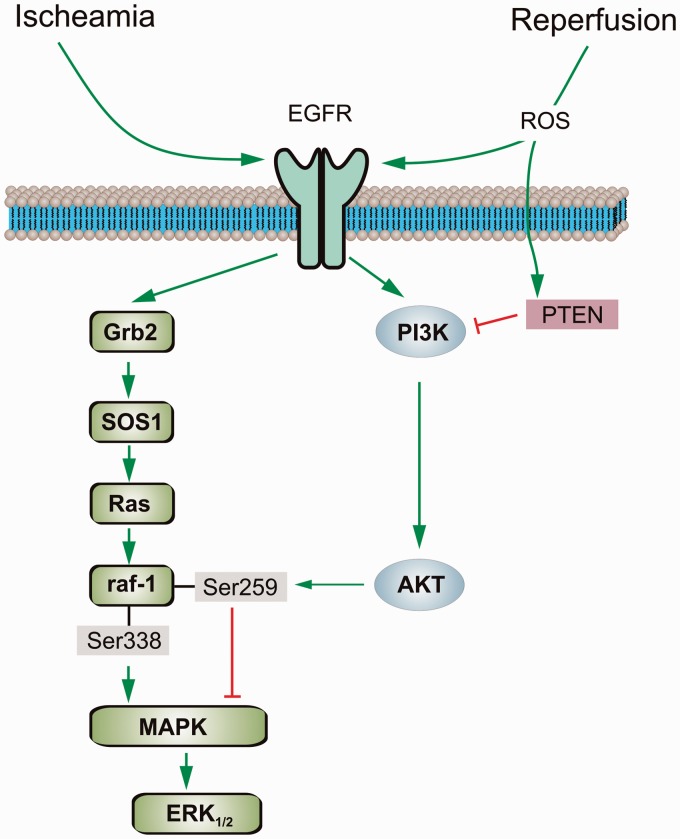
Figure 10.
Diagram of crosstalk between Raf/MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signal pathways during brain ischemia and reperfusion. Ischemia induces EGFR transactivation and phosphorylation at Y1173, Y845, and Y1045. The activation of EGFR, in turn, significantly stimulates PI3K/AKT signal pathway. Subsequently, AKT phosphorylates Raf-1 at its inhibitory phosphorylation site Ser259 and inhibits Raf-1 activity. The inhibition of Raf-1 leads to inactivation of its downstream signal MAPK/ERK. During reperfusion, ROS stimulates both EGFR and PTEN. The latter, in turn, inhibits PI3K/AKT signal pathway and restores the activity of Raf-1/MAPK/ERK1/2 signal pathway, which is responsible for reperfusion-induced cell damage. EGFR = epidermal growth factor receptor; ROS = reactive oxygen species; PTEN = phosphatase and tensin homolog; SOS1 = Son of sevenless 1; AKT = protein kinase B; MAPK = mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK = extracellular signal-regulated kinase.