Figure 10.
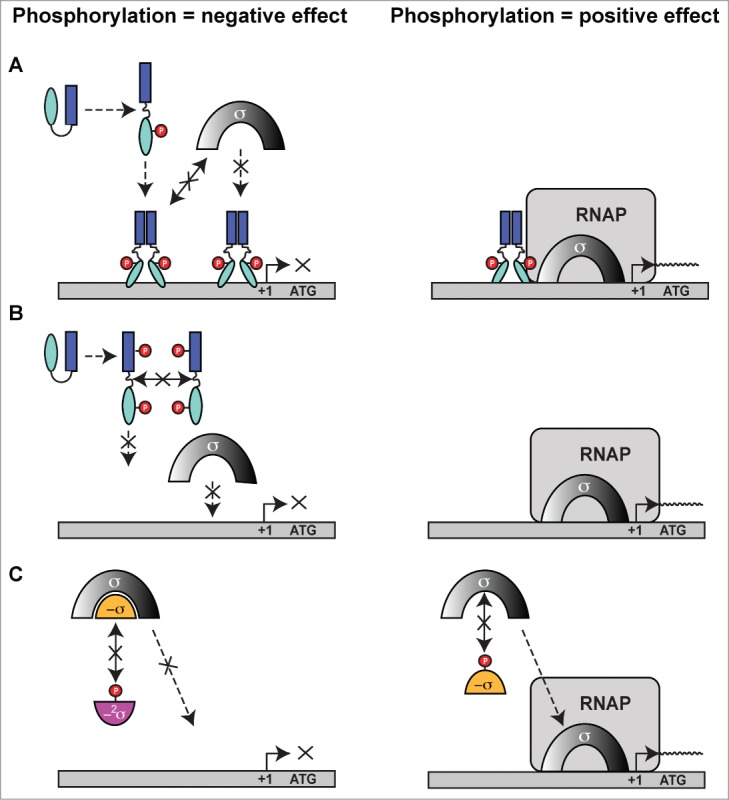
Possible mechanisms of eSTK/eSTP regulation of transcription. (A) eSTK phosphorylation of a transcription factor can cause either a negative effect (left) or positive effect (right) on the recruitment of transcriptional machinery through direct sigma factor and/or RNA polymerase (RNAP) interactions. (B) eSTK phosphorylation can also directly influence transcription factor binding to target DNA by either obstructing sister monomer interactions, or by directly affecting its physical hydrogen-bonding to target DNA. These influences can result in either a negative (left panel) or positive (right panel) effect on σ-factor/RNAP recruitment. (C) eSTK phosphorylation of both anti-sigma factors (-σ) and anti-anti-sigma factors (−2σ) can result in negative (left) or positive (right) effects on σ-factor/RNAP recruitment.
