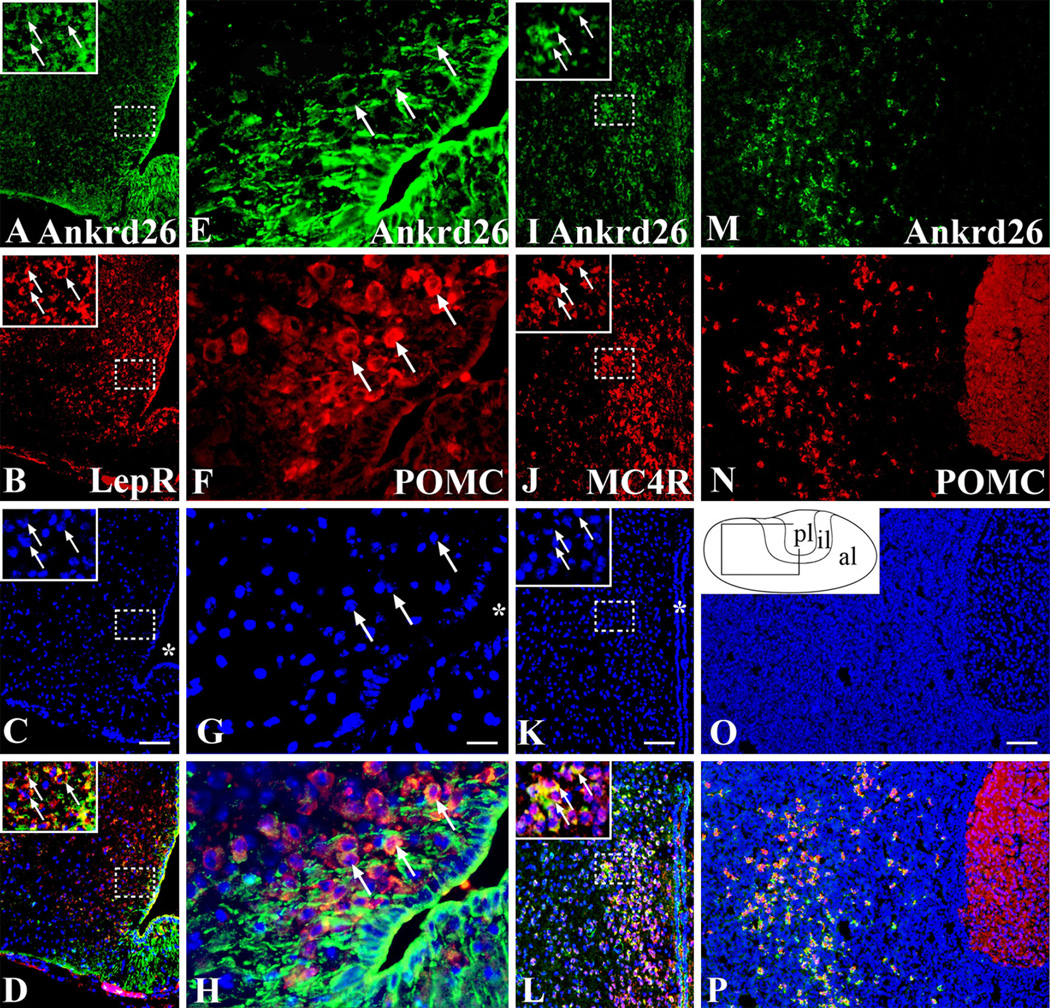
Fig. 3.
Expression of Ankrd26 in the melanocortin pathway and in the pituitary gland. Dual labeling IHC demonstrating Ankrd26 expression in the key cell populations of the melanocortin pathway. Ankrd26 immunostaining (green) is shown in the upper row (a, e, i, m). a–d In the ARC, LepR-positive cells (b, red) are co-labeled with Ankrd26 (a, green) as shown in the merged image (d). The magnified area in the insets is indicated by dashed boxes. Arrows show double-labeled cells. Scale bar 100 µm. e–h Immunostaining for POMC (f, red) and Ankrd26 (e, green) in the ARC shows many double-labeled cells (h, merged image) (marked by arrows). 409 magnification, scale bar 15 µm. i–l Immunostaining for MC4R (j, red) and Ankrd26 (i, green) in the PVN reveals numerous double-stained cells (l, merged image). The magnified area in the insets is indicated by dashed boxes. Arrows show double-labeled cells. Scale bar 100 µm. m–p In the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland all POMC-positive cells (n, red) are stained for Ankrd26 (p, merged image). Scale bar 100 µm. Inset in o is the schematic drawing of the pituitary gland. Al anterior lobe, il intermediate lobe, pl posterior lobe. In c, g, k and o nuclei are visualized with DAPI (blue). Asterisk in c, g, and k indicates the third ventricle