Fig. 4.
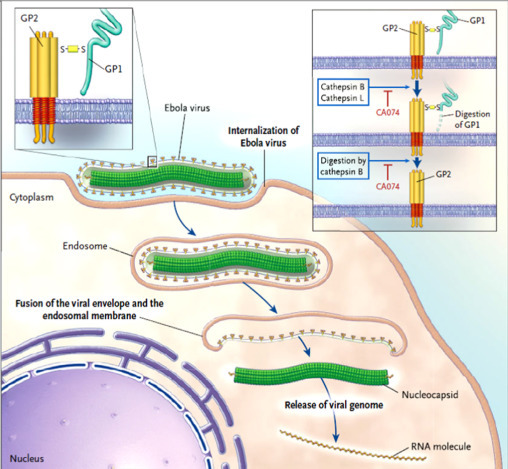
Entry pathway of Ebola Virus into host cell (Kawaoka, 2005). Upon binding to cell-surface receptors, Ebola gets internalized in endosome. Within endosome, endosomal proteases: cathepsin B and cathepsin L, slash the viral GP1 protein into N-terminal fragment and then cathepsin B digests it further into only GP2. GP2 aids in the fusion of viral envelope and endosomal membrane, releasing viral genome into the cytoplasm. Upon release the proteolysis of GP1 is prevented by CA074 (inhibitor) and therefore infection advances.
