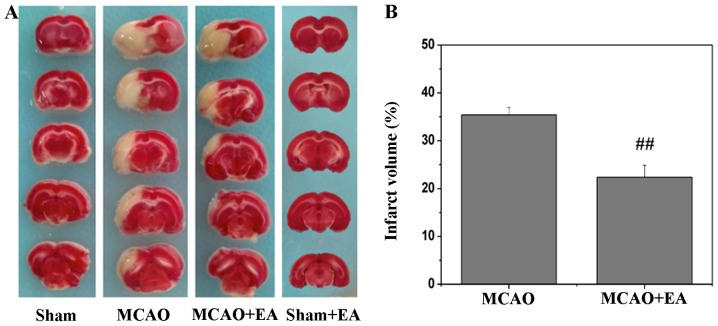
Figure 1.
Effects of electro-acupuncture (EA) on cerebral infarction after stroke. (A) Cerebral tissues from each group were coronally sectioned into 2-mm-thick slices and then processed for 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining. Normal areas of the brain were stained deep red, indicating intact mitochondrial function, whereas the infarct areas remained unstained. Representative images were captured using a high-resolution digital camera. (B) Infarct volume was quantified using the Motic Med 6.0 system, and is presented as a percentage of the total brain volume. Data shown are the means ± SEM from 5 individual rats in each group. ##P<0.01 vs. MCAO group. Sham, sham operation, control; MCAO, middle cerebral artery occlusion.