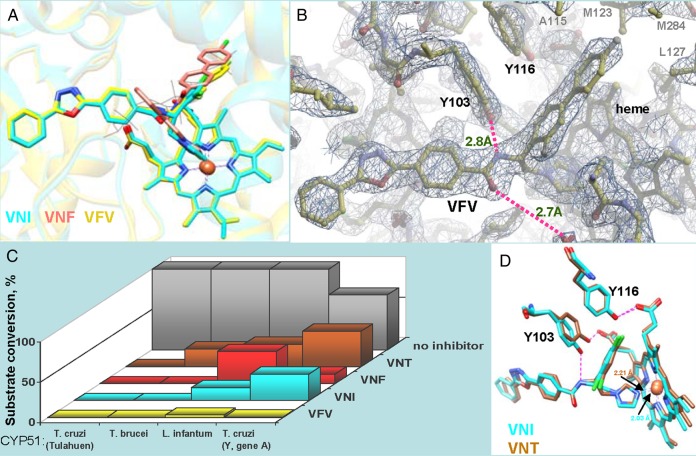
Figure 2.
Structural basis for the broader antiprotozoan spectrum of action of VFV. A, Binding modes of VNI (cyan), VNF (salmon), and VFV (yellow) in the superimposed CYP51 costructures (PDB ID 3GW9, 3KSW, and 4G7G, respectively). The secondary structural elements of the protein are seen as semitransparent ribbons of the corresponding colors. A molecule of the CYP51 substrate eburicol is delineated in gray lines as a reference. B, 2Fo-Fc electron density map (1.5σ) of the VFV-bound area in the CYP51 costructure (PDB ID 4G7G). The H-bond network is shown in purple, the distances are marked. C, Inhibitory effects of VNI, VNF, VNT, and VFV on sterol 14α-demethylase activity of 4 protozoan CYP51 orthologs at 1/1/50 molar ratio inhibitor/enzyme/substrate [16, 17]. P450 concentration 0.5 µM; 1-hour reaction. T. brucei cytochrome P450 reductase [27] was used as the electron donor. While all the derivatives are potent inhibitors of Tulahuen T. cruzi CYP51, only VFV reveals about the same strong potency against different tested protozoan CYP51 orthologs, including L. infantum and Y-T. cruzi CYP51A (Y strain T. cruzi has 2 CYP51 genes, gene A was shown to be resistant to inhibition [28]). D, In 1 of the 4 T. brucei CYP51-VNT molecules (4G3J, brown), the side chain of Y103 remains in contact with the heme propionate, and the H-bond network with the inhibitor is not formed, which is in good agreement with the weaker inhibitory effect of VNT on T. brucei CYP51 activity (shown in panel C). Superimposition with VNI in 3GW9, cyan. The Fe-N coordination bonds are 2.21Å and 2.03Å, respectively.