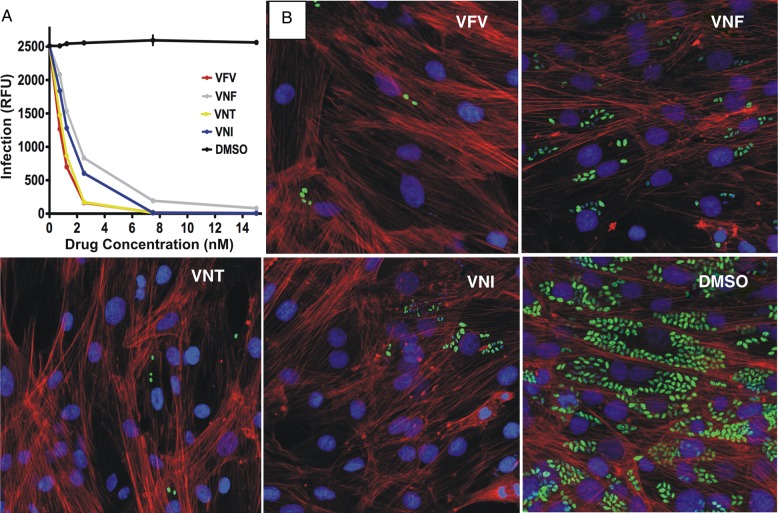
Figure 3.
Cellular effects of CYP51 inhibitors in Tulahuen T. cruzi infected cardiomyocytes. A, Comparative dose-dependent clearance of the parasite. Cardiomyocyte monolayers were exposed to green fluorescent protein–expressing Tulahuen trypomastigotes (10 parasites per cell) for 24 hours and then treated with 1–16 nM VNI, VNF, VFV, VNT, or DMSO. The infection was quantified by determining the fluorescence level of parasites expressing green fluorescent protein, indicated as relative fluorescence units (RFUs) 72 hours after infection. Data represent the mean values ± SEM of the results from triplicate samples. B, Fluorescence microscopic observations of Tulahuen T. cruzi inside cardiomyocytes treated with 4 nM of VNI, VNF, VFV, VNT, or DMSO 72 hours after infection. The monolayers were fixed with 2.5% paraformaldehyde and stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole to visualize DNA, and with Alexa fluor to visualize actin myofibrils. Trypanosoma cruzi amastigotes are green, cardiomyocyte nuclei are blue, and cardiomyocyte actin myofibrils are red. Abbreviations: DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; SEM, standard error of the mean.