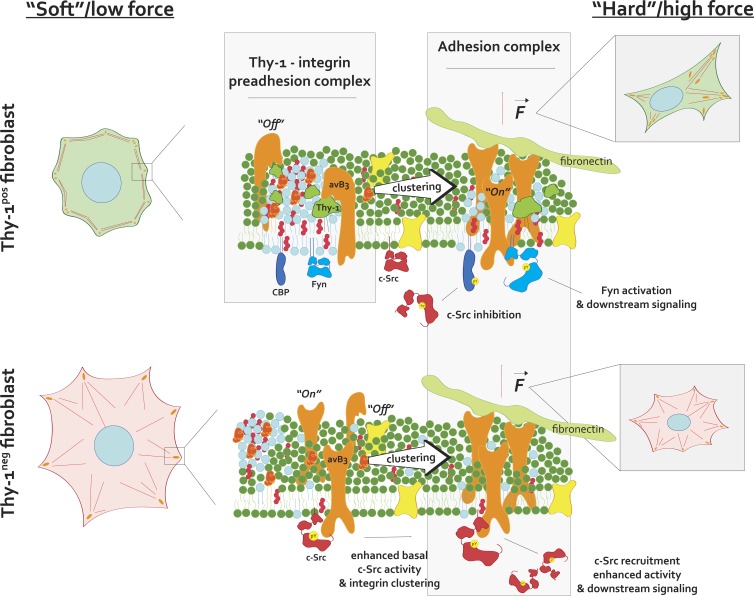
Figure 7.
A mechanistic model of Thy-1’s effects on integrin avidity and signaling. Thy-1 binds αv integrins preferentially in their inactive, “off” state, which couples integrins with membrane raft domains and their localized signaling molecules, such as Fyn and Cbp, before FN recognition (top, left). FN binding and receptor clustering enriches for these domains within growing FAs while promoting conformation-dependent integrin/SFK accessibility of binding motifs and sensitive responses to stimuli (e.g., force; top, right). In the absence of Thy-1, a higher probability of αv integrin binding to FN exists, thus eliciting elevated levels of baseline integrin signaling, potentially through c-Src recruitment and activation (bottom, left). As a result of decoupling of integrin and membrane rafts, raft-associated molecules (Fyn, Cbp) are no longer recruited to growing FAs and sensitive signaling (e.g., Cbp-dependent negative feedback on c-Src regulation and force-dependent Fyn activation) is not as prominent (bottom, right).