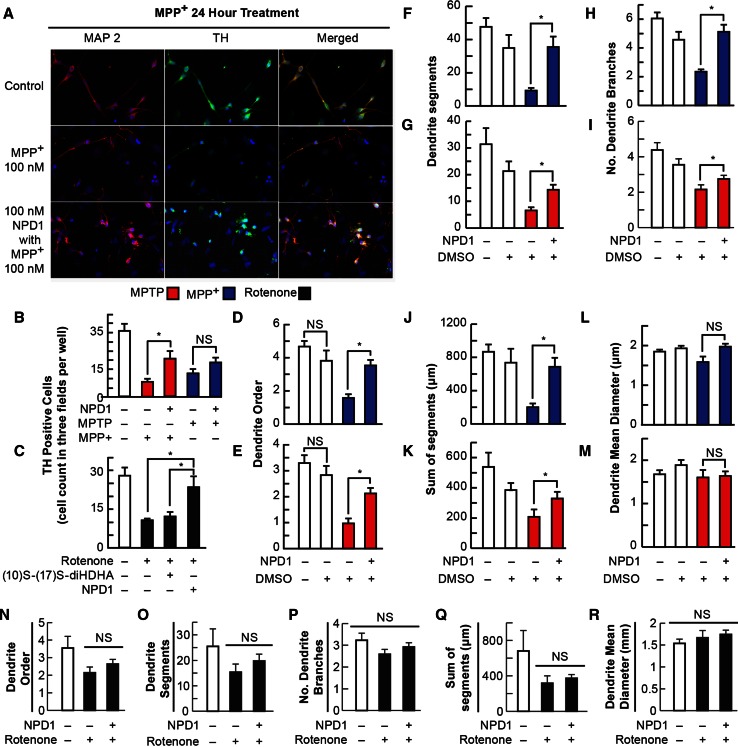
Fig. 1.
NPD1 promotes survival and prevents dendrite dystrophy of dopaminergic neurons upon addition of MPTP, MPP+, and rotenone. a–c Neuron survival was measured by a direct count of tyrosine hydroxylase-positive neurons per random field by triplicate per well in at least two wells per condition in two independent experiments. a Representative images of mesencephalic neuronal culture neurons stained with MAP2 (red first column) and tyrosine hydroxylase (green second column); nuclei are blue. b, c Tyrosine hydroxylase-positive cells after 24-h 100 µM MPP+ or 100 µM MPTP (b) and 100 nM rotenone (c) treatment in the presence or absence of 100 nM NPD1 (b, c) or 10S–17S-diHDHA stereoisomer (c). d–m Neurons that survived MPP+ or MPTP in the presence of NPD1 showed a better dendritic architecture than those that were not treated with NPD1. d, e Maximum dendritic order, f, g number of segments, h, i number of branches, j, k sum of the length of all the segments per neuron, and l, m the mean diameter of the dendrites in MPP+- (d, f, h, j, l) or MPTP- (e, g, i, k, m) treated cells in the presence or absence of NPD1. DMSO was added as vehicle control. Isolated TH-positive neurons from three random fields per well in two wells per experiment were traced using IMARIS 7. Two experiments were pooled together. n–r TH-positive neurons that survived 100 nM rotenone treatment for 24 h: n maximum dendritic order, o number of segments, p number of branches, q sum of the length of all the segments per neuron, and r the mean diameter of the dendrites. Total neurons included for d, f, h, j, l were control N = 22, DMSO N = 11, MPP+ N = 25, and MPP+ + NPD1 N = 37. For e, g, i, k, m: control N = 23, DMSO N = 16, MPP+ N = 17 and MPP+ + NPD1 N = 30. For n–r, control N = 10, rotenone +, rotenone + NPD1 N = 33, and rotenone alone N = 18. Bars represent the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, NS non-significant P value