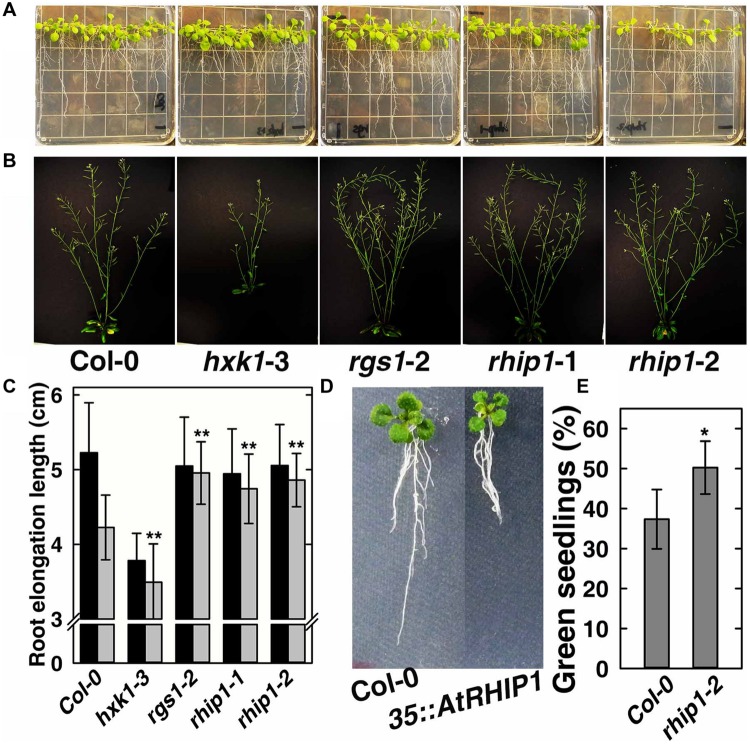
FIGURE 7.
rhip1 mutants share growth phenotypes with the rgs1-2 null mutant. (A) 2-week-old Col-0, hxk1-3, rgs1-2, rhip1-1, and rhip1-2 plants grown in 1/4 × MS medium supplemented with 1% D-glucose (w/v) and grown at 200 μmol s-1 m-2 in 8/16 h (L/D). (B) 5-week-old Col-0, hxk1-3, rgs1-2, rhip1-1, and rhip1-2 plants grown at 160 μmol s-1 m-2 in 16/8 h (L/D). (C) Comparison of root elongation of Col-0, hxk1-3, rgs1-2, rhip1-1, and rhip1-2 seedlings transferred to 1/4 × MS medium supplemented with 0.25% (black) or 3% (gray) w/v D-glucose and grown at 70 μmol s-1 m-2 in 16/8 h (L/D). Values indicate means ± SD (n = 10–18) from a representative experiment. For the 3% D-glucose treatment, ANOVA single factor analysis (α = 0.05) was conducted to compare values to the Col-0. ∗∗P < 0.01. (D) 2-week-old Col-0 and 35S::YFP-RHIP1 plants grown in 1/4 × MS medium supplemented with 3% D-glucose (w/v). (E) Green seedling assay of the rhip1-2 mutant. The assay was performed as described in Section “Material and Methods.” The average percentage of seedlings showing green cotyledons was determined and presented with means ± SD from one representative experiment of 4 biological replications. ANOVA single factor analysis (α = 0.05) was conducted to compare values to the Col-0. ∗P < 0.05.