FIGURE 1.
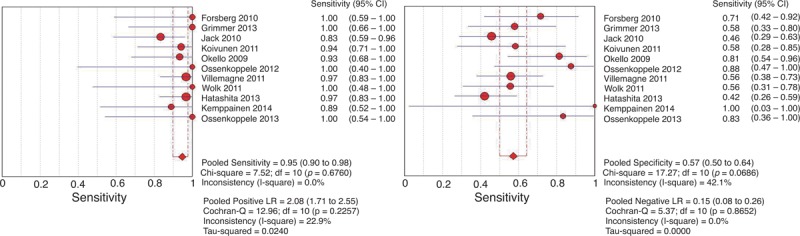
Forest plot of 11C-PIB-PET for predicting conversion to AD in patients with MCI. The figure shows the 2 × 2 table (TP, FP, FN, and TN) for each study, which form the basis for statistical analyses. Study-specific estimates of sensitivity and specificity are shown (represented as squares) with 95% CIs (represented as lines). Using Meta-DiSc, these estimates (and CIs) are also shown graphically. This figure demonstrates the greater uncertainty (indicated by CI width) and variability (indicated by the scatter of point estimates) in specificity compared with sensitivity. For the included studies, the sensitivities ranged from 83.3% to 100%, whereas the specificities ranged from 42.1% to 100%. The pooled sensitivity was 94.7% (95% CI: 89.8%–97.7%), and the pooled specificity was 57.2% (95% CI: 50.1%–64.2%). 11C-PIB-PET = 11C-Pittsburgh compound B positron emission tomography, 95% CI = 95% confidence interval, AD = Alzheimer disease, DOR = diagnostic odds ratio, FN = false-negative, FP = false-positive, MCI = mild cognitive impairment, TN = true-negative, TP = true-positive.
