Fig. 9. A 77-year-old male with a carotid plaque with intraplaque neovascularisation.
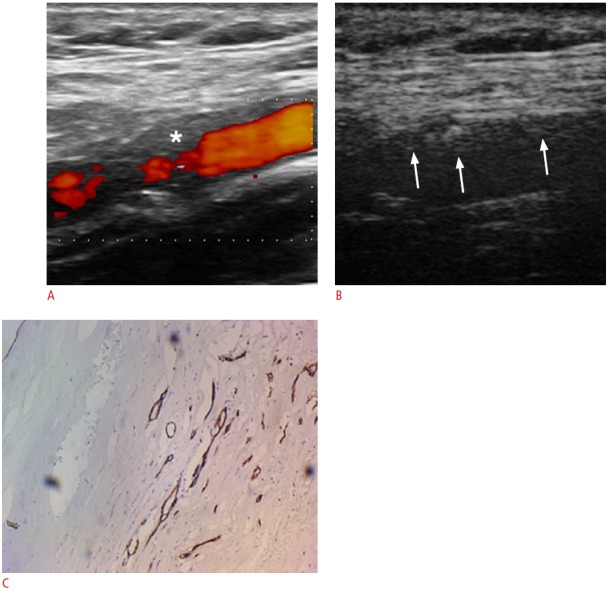
A. Power Doppler imaging as well as the other conventional ultrasonographic techniques (not presented) identified a hypoechoic plaque in the proximal part of the internal carotid artery (asterisk). B. Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography reveals the presence of moving linear echoes inside the plaque, which represent moving microbubbles inside the neovessels and thus neovascularisation (arrows). The identification of neovascularisation is more prominent in the proximal wall of the vessel than the distal one. C. The corresponding histologic image with immunohistochemical staining with CD34 shows the presence of intraplaque neovessels (×10).
