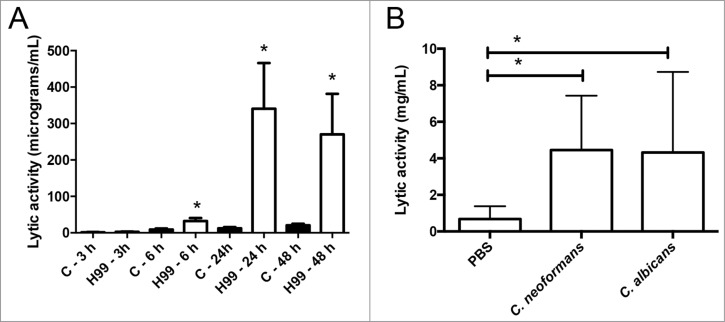
Figure 1.
Effect of C. neoformans on the antimicrobial activity of the G. mellonella hemolymph. (A) Groups of 10 G. mellonella were infected with C. neoformans H99 strain (106 cells/G. mellonella) or with PBS (C), and then they were incubated at 37°C. The lytic activity of the hemolymph was evaluated as described in Material and Methods after different timepoints. Asterisks denote statistical difference between the sample and the corresponding control G. mellonella larvae treated with PBS. (B) G. mellonella larvae were infected with C. neoformans H99 or C. albicans SC5314 strain (105 cells per G. mellonella) and incubated at 37°C overnight. Then, the lytic of the hemolymph was evaluated. Asterisks denote statistical difference between the sample and the control G. mellonella treated with PBS.