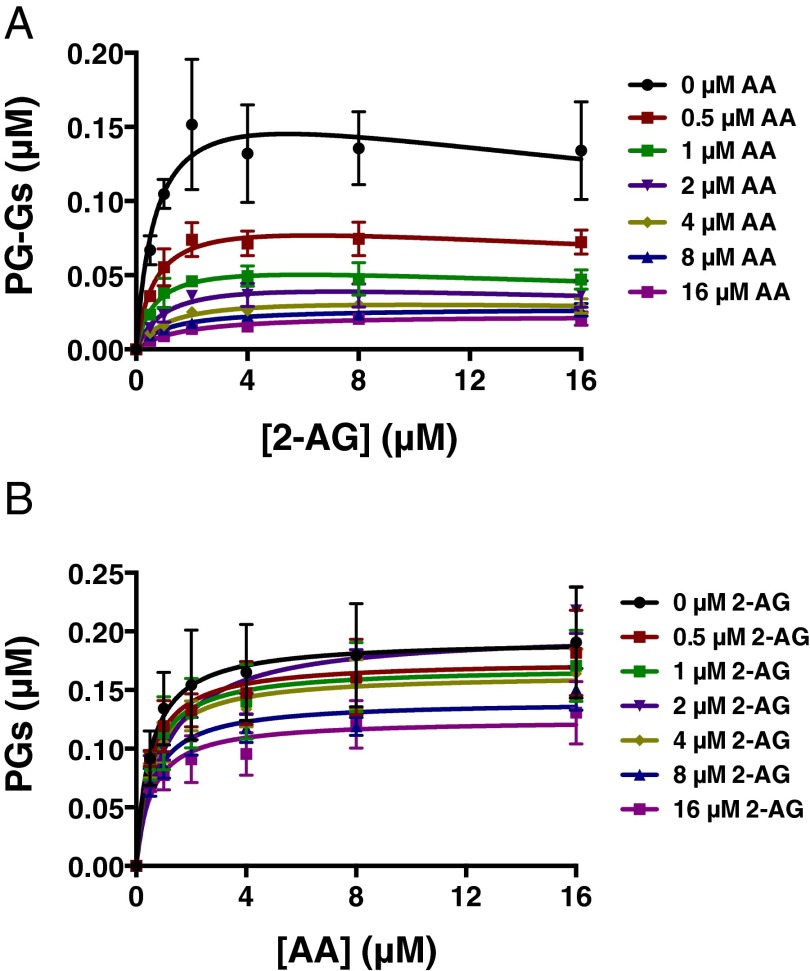
Fig. 3.
AA suppresses 2-AG oxygenation by mCOX-2 in vitro. The indicated concentrations of premixed 2-AG and AA with 1 μM PPHP were incubated with 15 nM mCOX-2 for 10 s. PGs and PG-Gs were quantified by LC-MS/MS. Results are depicted as PG-G formation as a function of increasing 2-AG concentration in the presence of various amounts of AA (A) and PG formation as a function of increasing AA concentration in the presence of various amounts of 2-AG (B). Results are the mean ± SD of triplicate determinations. Kinetic parameters for oxygenation of 2-AG in the absence of AA were as follows: Km = 0.71 ± 0.37 μM, kcat = 1.2 ± 0.2 s−1, and KI = 42 ± 38 μM. Kinetic parameters for oxygenation of AA in the absence of 2-AG were as follows: Km = 0.51 ± 0.18 μM and kcat = 1.3 ± 0.1 s−1.