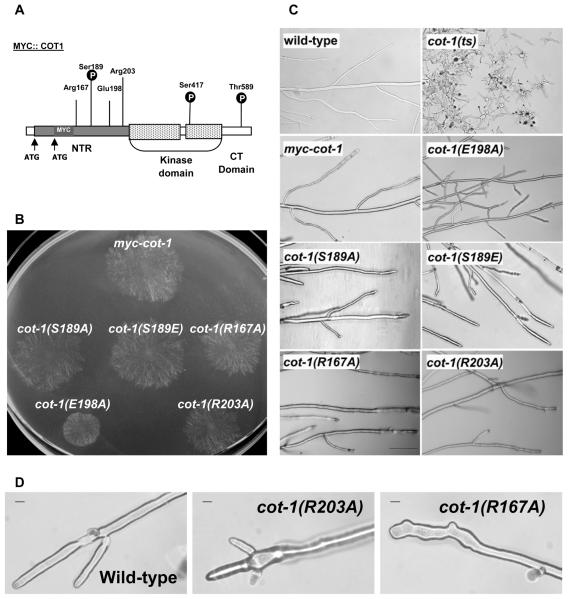
Fig. 1.
Conserved residues within the N-terminal region of COT1 affect fungal morphology.
A. Schematic summary of amino acid alterations introduced into COT1 NTR. The two highly conserved phosphorylation sites at the kinase domain (Ser417) and C Terminal domain (Thr589) are also shown. Grey box represents the NTR and a dotted box represents the kinase domain. The residues’ numbers refer to the COT1 protein (long transcript) without the Myc tag.
B. Growth of myc-cot-1 and the NTR mutants harbouring the different Myc-tagged alleles of cot-1. Cultures were grown overnight at 34°C.
C. Hyphal morphology at the edge of the colony of wild-type, cot-1(ts), myc-cot-1 and the NTR point-mutation strains cultured overnight at 34°C. Bar = 100 μm.
D. Microscopic images of myc-cot-1, cot-1(R167A) and cot-1(R203A) hyphal tips grown at 34°C. Bar represents 10 μm.