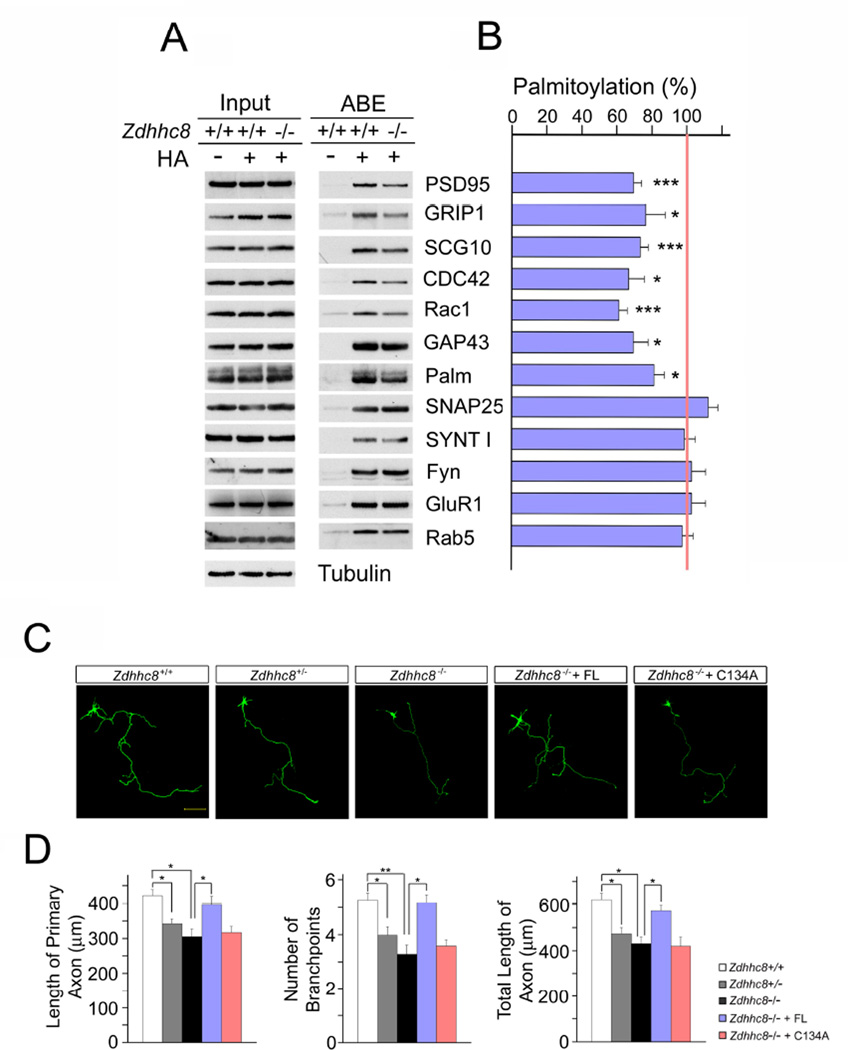
Figure 1. Acyl-biotinyl exchange (ABE) analysis of neuronal protein palmitoylation and axonal alterations in Zdhhc8-deficient cortical neurons.
(A) Palmitoylation levels of selected palmitoyl protein candidate substrates. Proteins, ABE-purified from cultured cortical neurons from WT and Zdhhc8−/− mice, both in the presence (+) and absence (-) of hydroxylamine (HA), were analyzed by western blotting using the indicated specific antibodies. Palmitoylated proteins are expected to show HA-dependent detection. As a control, a portion of the starting protein sample (prior to ABE purification) was also screened. Palm, paralemmin; SYNT I, synaptotagmin I.
(B) Quantification of the palmitoylation changes induced by Zdhhc8−/− deficiency. Protein levels measured from the purified palmitoyl-protein samples were normalized to levels measured from the corresponding input of substrates.
(C) Representative images of Zdhhc8-dependent axonal deficits in cortical neurons expressing EGFP at DIV4. Zdhhc8−/− cortical neurons were transfected with plasmids expressing EGFP and ZDHHC8-FL or ZDHHC8-C134A at DIV2 and fixed at DIV4. Scale bar, 50 µm.
(D) Quantification of axon length and branch points number in Zdhhc8-deficient cortical neurons. Transfection of ZDHHC8-FL, but not ZDHHC8-C134A, restored axon length and branchpoints number. Data are shown as means ± s.e.m. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.001; ***, P < 0.0001; Student’s t-test.
See also Figure S1.