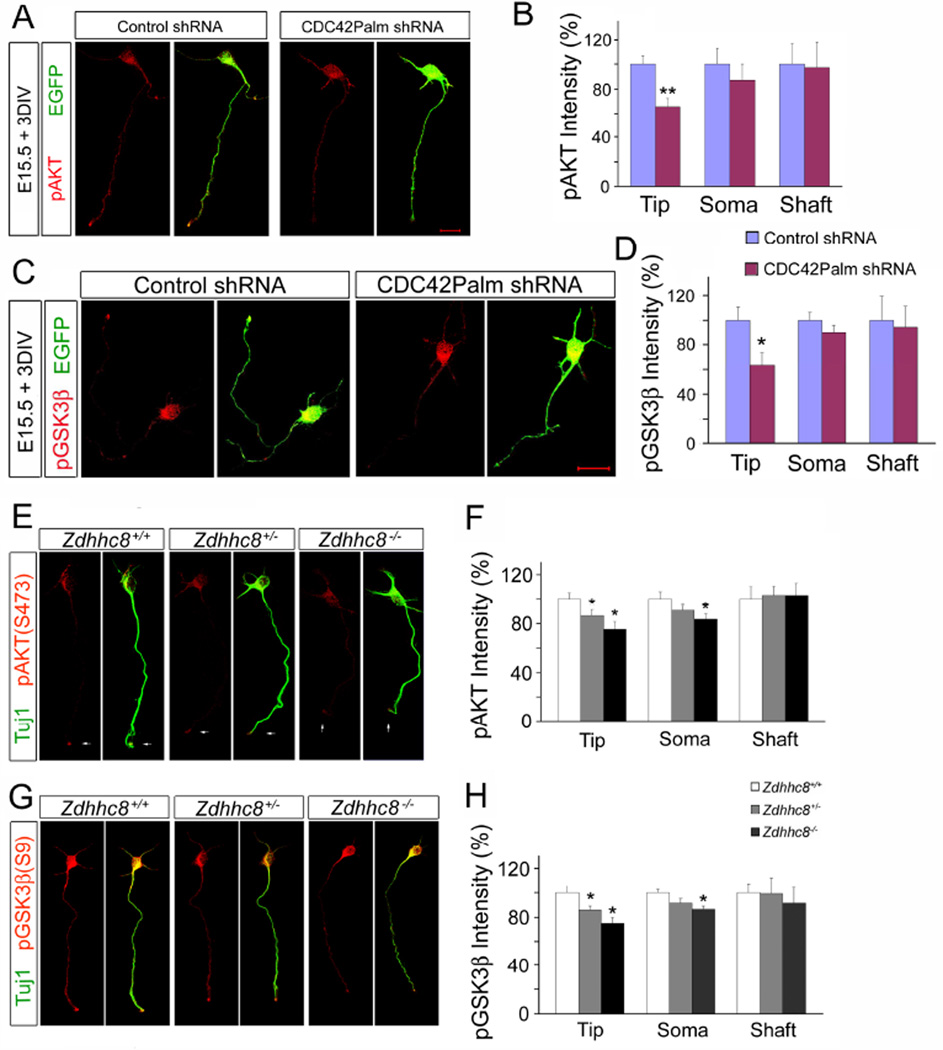
Figure 7. Zdhhc8 deficiency disrupts AKT/GSK3β signaling cascade.
(A) Representative cortical neurons stained for pAKT (S473) (red) and EGFP (green) at DIV3 following ex utero electroporation of shRNA targeting CDC42Palm or scrambled shRNA.
(B) Quantification of fluorescence intensity reveals that knockdown of CDC42Palm reduces pAKT (S473) intensity at the tip of the axon.
(C) Representative cortical neurons stained for pGSK3β (S9) (red) and EGFP (green) at DIV3 following ex utero electroporation of shRNA targeting CDC42Palm or scrambled shRNA.
(D) Quantification of fluorescence intensity reveals that knockdown of CDC42Palm reduces pGSK3β (S9) intensity at the tip of the axon.
(E) Representative images of DIV3 cortical neurons immunostained with pAKT(S473) (red) and neuronal marker Tuj1(green) from Zdhhc8-deficient and control mice.
(F) Quantification of fluorescence intensity reveals that Zdhhc8 deficiency reduces pAKT(S473) intensity at the tip of axon.
(G) Representative images of DIV3 cortical neurons immunostained with pGSK3β(S9) (red) and neuronal marker Tuj1(green) from Zdhhc8-deficient and control mice.
(H) Quantification of axon tip fluorescence intensity reveals that Zdhhc8 deficiency reduces pGSK3b(S9) intensity at the tip of axon.