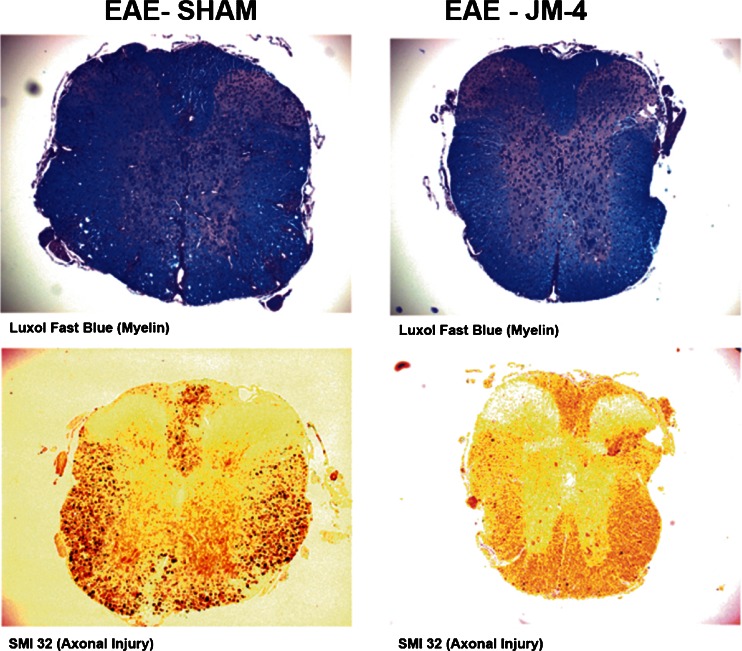
Fig. 4.
JM-4 protects against spinal cord demyelination and axonal injury in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). SJL/J mice immunized with proteolipid protein (PLP) peptide were treated with either JM-4 or phosphate-buffered saline for 7 days and spinal cords were collected to evaluate pathological differences by staining with Luxol fast blue for myelin, or labeled with SMI-32 antibody for nonphosphorylated neurofilament H, a marker of acute axonal injury. In EAE sham-treated animals, vacuolated regions could be seen in the white matter representing extensive demyelinated areas while JM-4 peptide treated EAE animals had little-to-no damage. Similarly, there was a pronounced reduction in number of injured SMI-32-stained axons in JM-4-treated EAE animals compared with sham-treated EAE controls. Blinded ranked pair analysis indicated the difference between JM-4-treated animals (n = 5–6 mice/group) and sham-treated control groups was significant (p < 0.05)