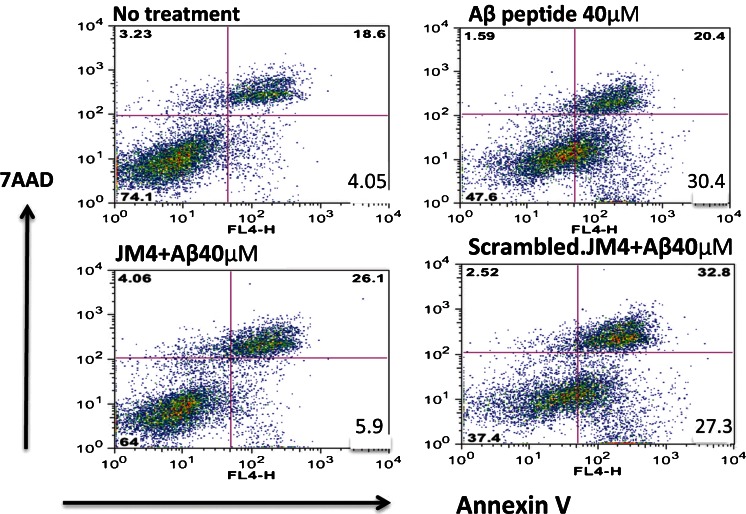
Fig. 6.
JM-4 attenuates cytotoxin-induced neuronal apoptosis. The neural crest-derived rat pheochromocytoma cell line PC12 was differentiated in vitro for 24 h. We pretreated cultures with JM-4 or scrambled JM-4 at a concentration of 1 μg/ml for 2 h, and then challenged the cells with Aβ25–35 peptide at 40 μM for 24 h. The cells were harvested and analyzed for death using 7-amino-actinomycin D (7-AAD), and stained for apoptosis with allophycocyanin conjugated–annexin V. The washed reacted cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. The lower right quadrant values within each graph show the size of the annexin V-positive apoptotic cell population. Toxic Aβ peptide exposure induced a massive increase in apoptotic cells (30.4%), whereas exposure to a reverse sequence Aβ35–25 molecule failed to induce apoptosis (data not shown). In contrast, JM-4 treatment strongly blocked apoptosis (reduced to 5.9%), whereas therapy with scrambled JM-4 failed to protect cells from apoptosis