Figure 1.
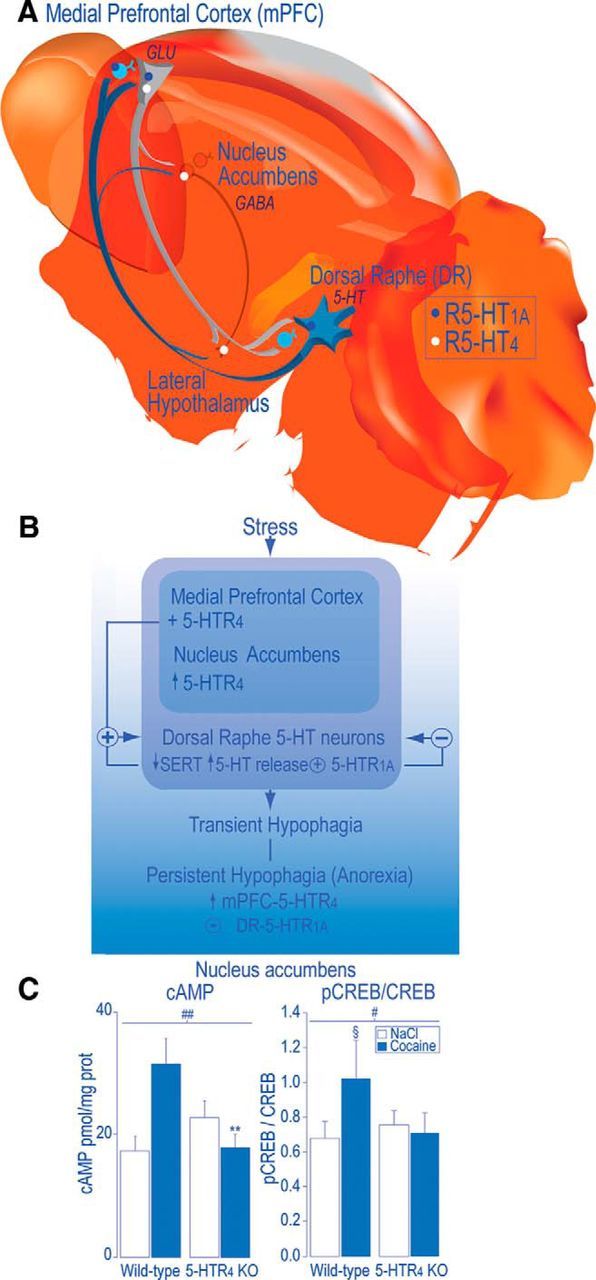
A working hypothesis: decision making to eat could partly depend on neural pathways concerned with dealing with stress. A, Efferent neurons of the mPFC mainly target the DR (Sesack et al., 1989; Peyron et al., 1998; Vertes, 2004) and contain glutamate (GLU) (Lee et al., 2003). With regard to the reciprocal descending projections, 5-HT neurons in the mPFC mainly arise from the DR and send axon collaterals to the NAc (Van Bockstaele et al., 1993). In the mPFC, 60% of pyramidal efferent neurons express both 5-HTR4 and 5-HTR1A mRNA (Feng et al., 2001). In the mPFC, 5-HTR4 mRNA are mainly expressed by GLU-expressing efferent neurons (Penas-Cazorla and Vilaro, 2014). In the NAc, 5-HTR4 are localized on GABA-expressing efferent neurons to the lateral hypothalamus (Jean et al., 2007). In the mPFC, the 5-HTR1A is localized, in the mPFC, in glutamatergic pyramidal efferent, local GABA-expressing interneurons (Czyrak et al., 2003; Amargós-Bosch et al., 2004; Santana et al., 2004) and on 5-HT terminals and, in the DR, on DR 5-HT neurons (Miquel et al., 1992; Pompeiano et al., 1992). B, From the mPFC, 5-HTR4 exert a tonic positive influence on the firing activity of DR 5-HT neurons in rodents (Lucas and Debonnel, 2002; Lucas et al., 2005; Conductier et al., 2006). From the DR and mPFC, 5-HTR1A exert a negative feedback on DR 5-HT neurons (Sprouse and Aghajanian, 1987; Haj-Dahmane et al., 1991; Bortolozzi et al., 2004). We found that mPFC 5-HTR4 overexpression induced decreases in the levels of plasma membrane 5-HT transporter (SERT) and increases in 5-HT release, which activates DR 5-HTR1A that prevent the transition from a transient to a sustained hypophagia (“early anorexia”), introducing anorexia as an antidepressant (5-HT accumulation resulting from 5-HTR1A desensitization and SERT reduction; Jean et al., 2012a, unpublished data). In addition, stimulation of 5-HTR4 in the NAc enhanced the activity of an addictive signaling pathway (cAMP/PKA/CART), which provokes anorexia and motor hyperactivity (Jean et al., 2007, 2012b), suggesting that neural substrates of anorexia are included in those of dependence. C, Consistently, acute intraperitoneal administration of cocaine (30 mg/kg) failed to increase, in the NAc, cAMP levels and pCREB/CREB ratio, in 5-HTR4 KO compared with wild-type mice. Data are means ± SEM, n = 5–8 mice of both genotypes per each group. A significant treatment effect is noted: §p < 0.05, §§ p < 0.01 compared with NaCl, a genotype effect (*p < 0.05) and genotype × treatment interaction, # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 after significant two-way ANOVA. We posit that decreased activity of the mPFC-5-HTR4 (among many other factors) could favor a subcortical influence; that is, an autonomous control without adaptive decisional control regardless of the requirement for energy (Compan, 2013).
