FIGURE 1.
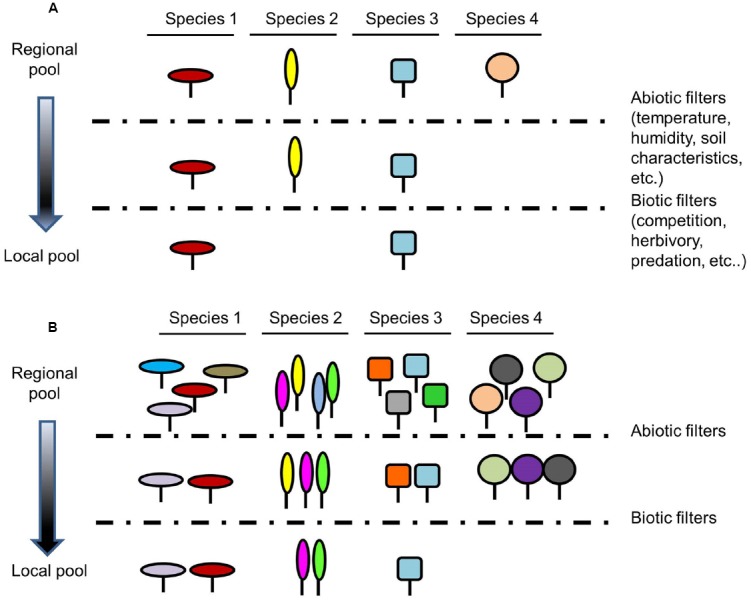
Influence of intraspecific variability in the filtering of potential species integrating a community. (A) classical community assembly theory without taking into account intraspecific variability and (B) community assembly theory incorporating intraspecific variability. Species with mean trait values matching the abiotic requirements and being either ecologically different or capable of tolerating competition will contribute to the eventual community. By incorporating intraspecific variability, more species will pass biotic and abiotic filters because they are able to adjust by phenotypic plasticity or simply because they are genetically variable so more species could join the community in (B) than in (A). Each shape represents a species and each color represents a given trait value within a species. Dashed lines represent abiotic and biotic filters.
